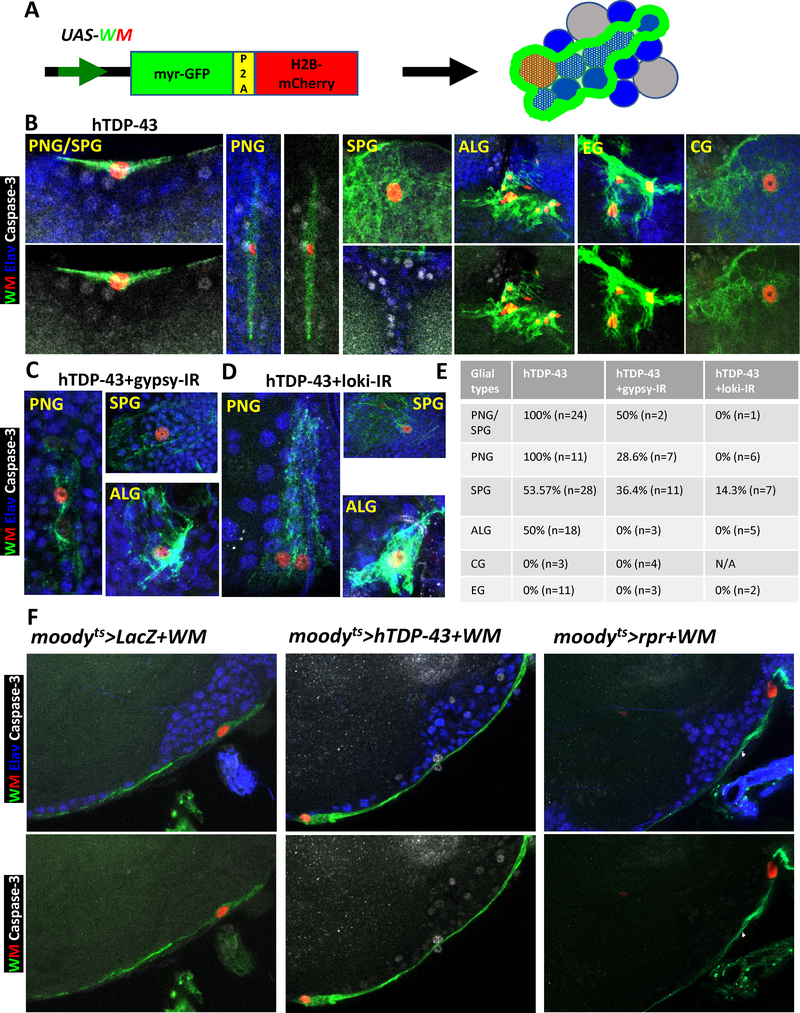
Figure 5. Focal Induction of Toxic Levels of hTDP-43 in Several Glial Sub-types Causes Apoptotic Cell Death in Adjacent Neurons.
(A) Schematic the dual label WM reporter to simultaneously mark glial nuclei (with H2B-mCherry) and glial membranes (with myr-GFP). This allowed identification of glial subtypes by morphology and location. Blue indicated neurons and grey represented unmarked glial cells.
(B) Co-induction of hTDP-43 and the dual WM reporter was stochastically initiated in glial cells via a transient induction of the hs-FLP recombinase and a FRT recombination sites flanked “FLP-Off-Gal80” cassette. The FLP-Off Gal80 was used in combination with the glial expressing repo-Gal4, along with UAS-driven hTDP-43 and WM. The hTDP-43 expressing clones were visualized with the nuclear H2B-mCherry (Red) and membrane myr-GFP (Green) from the WM reporter. The dual WM reporter allowed identification of the glial subtype for each clone. Apoptotic cell death signaling was monitored via an activated Caspase-3 antibody (White) and each neuronal nucleus was labeled with antibodies against the Elav marker (Blue). Perineurial glia (PNG), Subperineurial glia (SPG), Astrocyte-like glia (ALG), Cortex glia (CG) and Ensheathing glia (EG) were separately detected by this method. Scale bar=10μm. (See also STAR METHODS for detailed genotypes). We detect Caspase-3 labeled neurons adjacent to the majority of PNG, SPG and ALG clones expressing hTDP-43. This is not seen with clonal induction of pro-apoptotic genes (See Figure S5A).
(C) Gypsy-ERV expression levels were knocked down within hTDP-43 expressing glial clones via co-expression of the gypsy-IR. The WM dual reporter was used as in (A), to mark hTDP-43 expressing glia. All neuronal nuclei were labeled with an antibody against the Elav marker (Blue) and cell death signaling is revealed with an antibody against activated Caspase-3 (White). Knocking down gypsy-ERV expression significantly reduced the numbers of Caspase-3 labeled neurons (E). Perineurial glia (PNG), Subperineurial glia (SPG) and Astrocyte-like glia (ALG) were shown. Scale bar=10μm. (See also STAR METHODS for detail genotype).
(D) Chk2/Loki expression levels were knocked down within hTDP-43 expressing glial clones via co-expression of the Loki-IR. The WM dual reporter was used as in (A), to mark hTDP-43 expressing glia. All neuronal nuclei were labeled with an antibody against the Elav marker (Blue) and cell death signaling is revealed with an antibody against activated Caspase-3 (White). Knocking down Chk2/Loki expression significantly reduced the numbers of Caspase-3 labeled neurons (E). Perineurial glia (PNG), Subperineurial glia (SPG) and Astrocyte-like glia (ALG) were shown. Scale bar=10μm. (See also STAR METHODS for detail genotype).
(E) Quantification of the fraction of glial clones of each glial cell type for which nearby neurons are labeled with activated Caspase-3 from (B-D). Cases where we could not unambiguously distinguish PNG from SPG were grouped.
(F) Effects of post development induction of hTDP-43 in SPGs was examined on Caspase-3 signaling in nearby neurons. The hTDP-43 or nls-LacZ (control) were co-induced with WM in SPG glia using the moodyts TARGET method. Activated cell death signaling was visualized with an antibody against Caspase-3 (White). SPG nuclei were labeled with H2B-mCherry (Red) and membranes with myr-GFP (Green) from the WM reporter. All neuronal nuclei were labeled with an antibody against the Elav marker (Blue). In addition to Caspase-3 activation in nearby neurons, we also observed Caspase-3 label in PNG nuclei (White arrowhead), which lie just superficial to the SPG. Caspase-3 label was not observed in neurons with expression of the nls-LacZ control (moodyts>nls-LacZ+WM). In contrast, expression of hTDP-43 (moodyts>hTDP-43+WM) in SPG was associated with induction of activated Caspase-3 signaling in adjacent neurons. Direct activation cell death via induction of the pro-apoptotic gene rpr (moodyts>rpr+WM) within SPG did not cause cell death signaling within adjacent neurons. Scale bar=20μm. See also Figure S5.