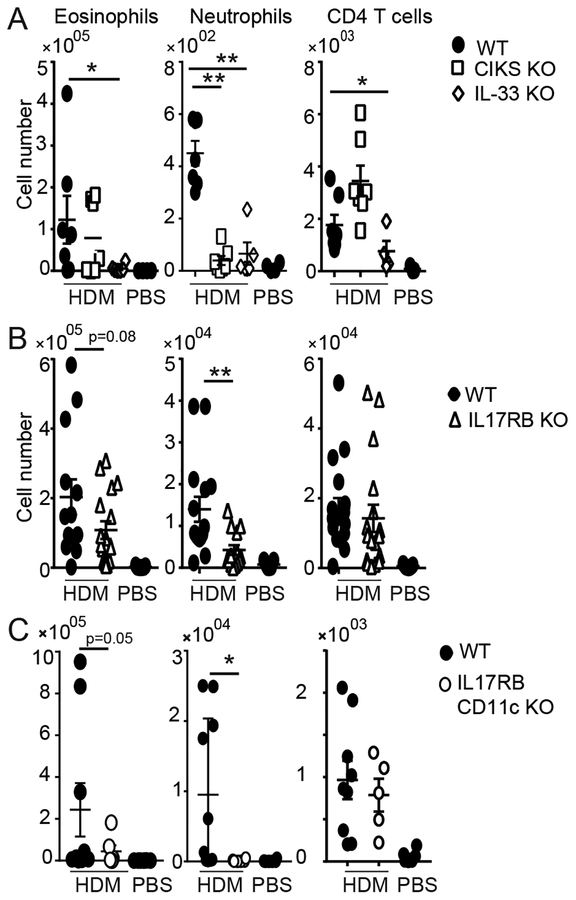
FIG 1.
IL-25 signaling contributes to chronic HDM-induced lung inflammation. Cellular counts in BALFs of WT, IL-33 KO and CIKS KO mice (A); WT and IL-17RB KO mice (B) and WT and IL-17RB CD11c KO mice (C) after chronic exposure to HDM (and PBS for WT; similar to PBS for KO mice). Eosinophils (SiglecF+ CD11c+ CD11b+); neutrophils (Ly6G+, CD11b+, CD11c−); T cells (CD4+ TCRβ+). Significance indicated for HDM-treated WT vs KO mice. Data are the mean ± sem of (A) two independent experiments with n=6–7 mice per group; (B) three independent experiments with n= 7–14; (C) two independent experiments with n=5–9. * p<0.05; **p<0.01