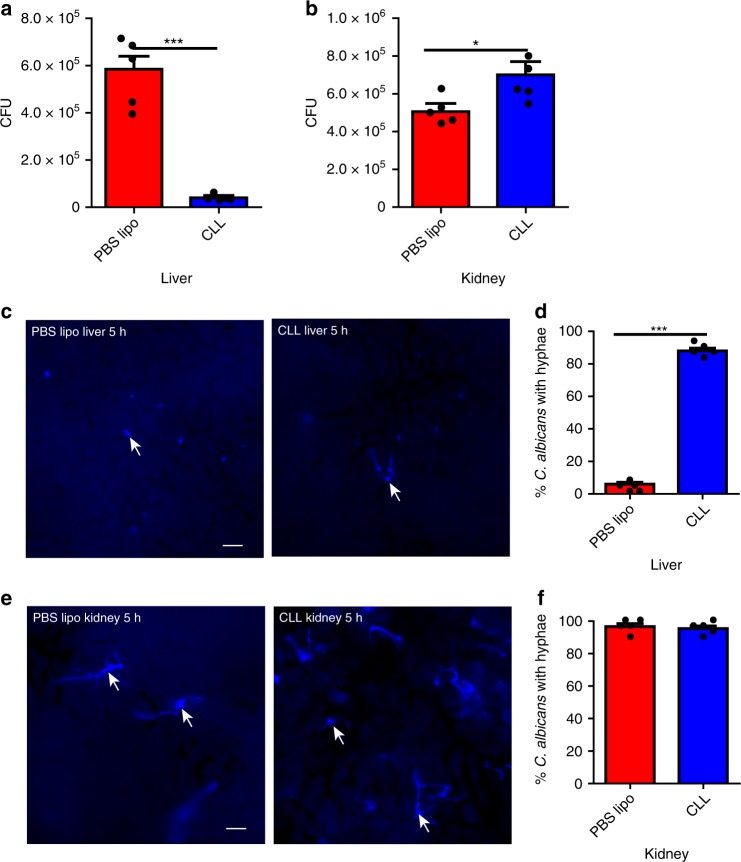
Fig. 7.
Liver KCs catch circulating C. albicans and inhibit its hyphal growth. a, b Mice (n = 5 mice/group) were treated with CLL or PBS lipo as control to deplete KCs and 24 h later i.v. infected with 5 × 106 C. albicans. CFU was enumerated 3 h post infection in the liver (a) and kidney (b). c, d Mice (n = 5 mice/group) were treated with CLL or PBS lipo as control to deplete KCs and 24 h later i.v. infected with 20 × 106 Uvitex 2B-labeled C. albicans. IVM was performed on the liver 5 h after infection to image the fungi. Representative images showing C. albicans in the liver (c). The percentage of C. albican with hyphae was determined by IVM (d). e, f Mice (n = 5 mice/group) were treated with CLL or PBS lipo as control to deplete KCs and 24 h later i.v. infected with 20 × 106 Uvitex 2B-labeled C. albicans. Kidney was excised 5 h post infection and immediately visualized under microscope. Representative images showing C. albicans in the kidney (e); The percentage of C. albicans with hyphae was determined (f). Scale bars: 25 µm. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. All data are from biologically distinct samples. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. p values were calculated by Student’s t test (a, b, d, f). Source data are provided as a Source Data file