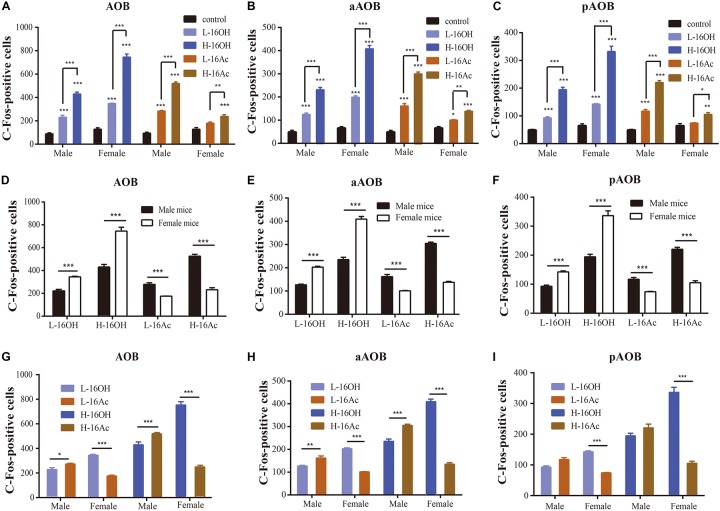
FIGURE 7.
Quantitative analysis of c-Fos+ AOB neurons of the male and female mice after exposure to 16OH and 16Ac. (A) Significantly more activated neurons were found in both male and female aAOB and pAOB following stimulation by all these four stimuli: low or high 16OH or 16Ac in comparison with the control samples except the L-16Ac in female mice (M-L-16OH vs. M-control, t = 6.780, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-control, t = 18.717, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 10.148, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 24.142, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-control, t = 11.996, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-control, t = 34.776, p = 0.000; F-L-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 2.364, p = 0.220; F-H-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 6.200, p = 0.000). H-16OH or H-16Ac evoked more c-Fos+ AOB neurons than the corresponding L-16OH and L-16Ac, respectively, in the mice of the same sex (M-H-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 11.937, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-L-16Ac, t = 13.994, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-L-16OH, t = 22.780, p = 0.000; F-H-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 3.836, p = 0.004). (B) Comparative analysis of the c-Fos+ cells in the aAOB of the same sex exposed to the same pheromone at either the low or high concentration. Significantly more activated neurons were found in both male and female aAOB following stimulation by all these four stimuli: low or high 16OH or 16Ac in comparison with the control samples whereas H-16OH or H-16Ac evoked more c-Fos+ aAOB neurons than the corresponding L-16OH and L-16Ac, respectively, in the mice of the same sex (M-L-16OH vs. M-control, t = 8.302, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-control, t = 20.212, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 11.910, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 12.126, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 27.836, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-L-16Ac, t = 10.078, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-control, t = 14.637, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-control, t = 37.370, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-L-16OH, t = 22.733, p = 0.000; F-L-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 3.499, p = 0.010; F-H-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 7.529, p = 0.000; F-H-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 4.030, p = 0.002). (C) Comparative analysis of the c-Fos+ cells in the pAOB of the same sex mice exposed to the same pheromone at the either low or high concentration (M-L-16OH vs. M-control, t = 4.266, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-control, t = 14.180, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 9.915, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 6.651, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 16.729, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-L-16Ac, t = 10.078, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-control, t = 7.596, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-control, t = 26.515, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-L-16OH, t = 18.919, p = 0.000; F-L-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 0.950, p = 1.000; F-H-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 3.639, p = 0.002; F-H-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 3.007, p = 0.041). (D) Comparative analysis of c-Fos+ neurons in the AOB of males versus females stimulated by 16OH or 16Ac at the low or high concentration (F-L-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 7.119, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. M-H-16OH, t = 17.963, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 5.881, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 16.039, p = 0.000). (E,F) Comparative analysis of c-Fos+ neurons to 16OH and 16Ac between male and female aAOB and pAOB, respectively. Female aAOB and pAOB responded more strongly to L- or H-16OH than male aAOB and pAOB, respectively, whereas male aAOB and pAOB did more strongly to L- or H-16Ac than female aAOB and pAOB, respectively (aAOB: F-L-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 8.307, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. M-H-16OH, t = 19.130, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 6.655, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 18.335, p = 0.000; pAOB: F-L-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 4.844, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. M-H-16OH, t = 13.849, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 4.187, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 11.258, p = 0.000). (G–I) Comparison of the efficacy of 16OH versus 16Ac on evoking the c-Fos response in the AOB. 16OH seemed to be more effective on the female AOB, aAOB, or pAOB than on the male counterparts while 16Ac was more effective on male AOB, aAOB, or pAOB than on the female counterparts (AOB: M-L-16Ac vs. M-L-16OH, t = 3.368, p = 0.015; M-H-16Ac vs. M-H-16OH, t = 5.426, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 9.632, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 28.576, p = 0.000; aAOB: M-L-16Ac vs. M-L-16OH, t = 3.825, p = 0.004; M-H-16Ac vs. M-H-16OH, t = 7.624, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 11.138, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 29.841, p = 0.000; pAOB: M-L-16Ac vs. M-L-16OH, t = 2.386, p = 0.209; M-H-16Ac vs. M-H-16OH, t = 2.548, p = 0.139; F-L-16OH vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 6.646, p = 0.000; F-H-16OH vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 22.559, p = 0.000). N = 6 for each group. All values are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.