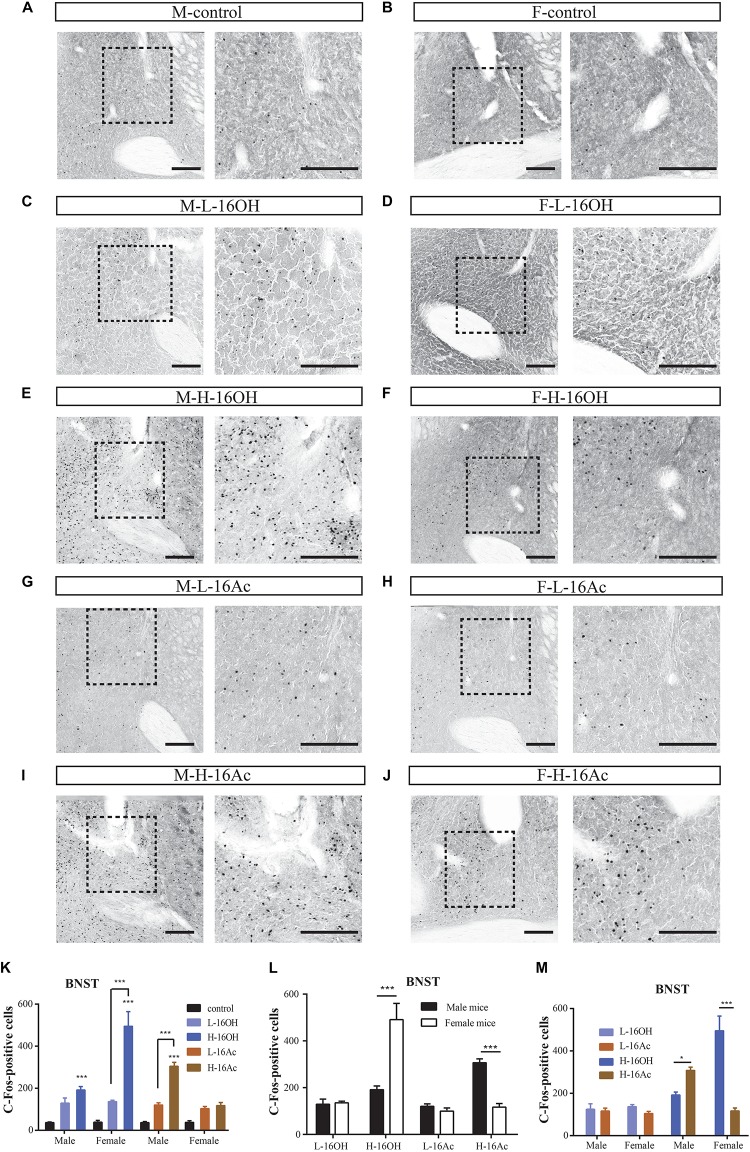
FIGURE 8.
Representative images and quantification of c-Fos+ neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) induced by 16OH and 16Ac. (A–J) Representative images and their insets of c-Fos+ cells in the BNST of male or female mice after exposure to 0.01% DCM-containing mineral oil (control), L-16OH, H-16OH, L-16Ac, and H-16Ac, respectively. Scale bar, 200 μm. (K) All treatments of H-16OH and H-16AC except H-16Ac on the female BNST evoked significantly stronger c-Fos immunoreactivity in the male and female BNST than the control (M-L-16OH vs. M-control, t = 2.598, p = 0.123; M-H-16OH vs. M-control, t = 4.358, p = 0.000; M-L-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 2.348, p = 0.228; M-H-16Ac vs. M-control, t = 7.577, p = 0.000; F-L-16OH vs. F-control, t = 2.737, p = 0.086; F-H-16OH vs. F-control, t = 12.793, p = 0.000; F-L-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 1.752, p = 0.860; F-H-16Ac vs. F-control, t = 2.172, p = 0.384). And H-16OH evoked significantly stronger c-Fos immunoreactivity than L-16OH in the female but not male mice whereas H-16Ac did so than L-16Ac in the opposite sex (F-H-16OH vs. F-L-16OH, t = 10.056, p = 0.000; M-H-16OH vs. M-L-16OH, t = 1.760, p = 0.845; M-H-16Ac vs. M-L-16Ac, t = 5.229, p = 0.000; F-H-16Ac vs. F-L-16Ac, t = 0.375, p = 1.000). (L) Comparison between sexes indicates that the female BNST responded more strongly to H-16OH than the male BNST whereas the male BNST did so to H-16Ac than the female BNST (F-H-16OH vs. M-H-16OH, t = 8.499, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 5.387, p = 0.000). (M) Comparison between the two pheromones indicates that H-16OH was more effective than H-16Ac on the female BNST whereas H-16Ac was more so than H-16OH on the male BNST (F-H-16OH vs. F-H-16Ac, t = 10.667, p = 0.000; M-H-16Ac vs. M-H-16OH, t = 3.219, p = 0.023). N = 6 for each group. All values are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.