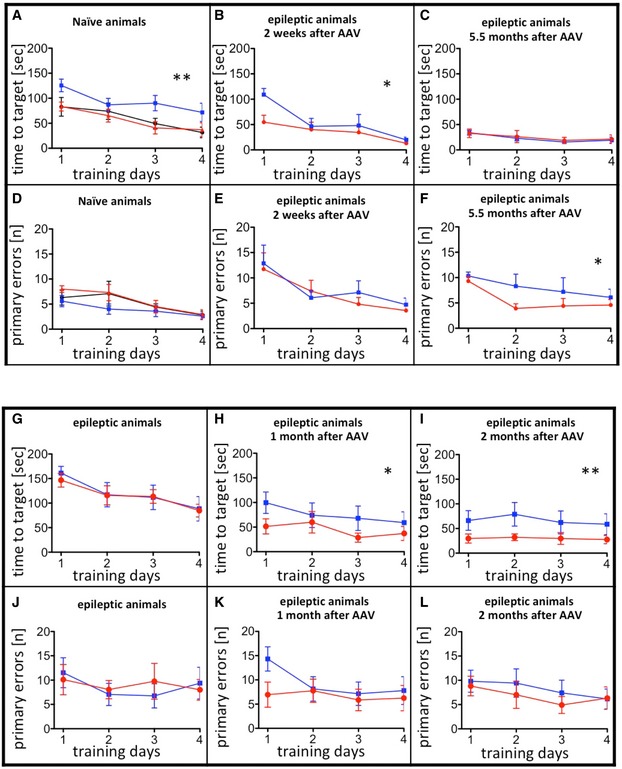
Spatial learning and memory were tested on the Barnes maze. Mice were trained on 4 consecutive days before testing memory. The acquisition of learning was monitored by assessment of the time needed to find the target hole (A–C; G–I) and the number of wrong holes visited before finding the correct one (primary errors; D–F: J–L) on each training day.
-
A–F
Unilateral injection of AAV‐pDyn (red) or AAV‐ΔGFP (blue) into naïve young adult mice compared with naive controls (black) is depicted in (A) and (D). Interestingly, AAV‐ΔGFP‐injected mice took longer to find the hole. Noteworthy, this had no impact on memory retrieval (Fig
2A–C). Mice treated 2 weeks after KA with AAV‐pDyn (red) or AAV‐ΔGFP (blue) (B, C, E, F) performed differently 2 weeks after vector application (B, E) in respect to time needed to target and 5.5 months (C, F) after treatment in respect to primary errors. The overall reduction in time needed to target is most probably due to the repeated testing of animals on the Barnes maze. The target hole was repositioned in each round, but the mice were familiar with the test per se.
-
G–L
A person not familiar with the mice assigned epileptic animals into two groups before testing on Barnes maze. No differences were observed between the two groups before vector treatment (G, J). By contrast, AAV‐pDyn (red)‐treated animals reached the target significantly faster than AAV‐ΔGFP (blue) 1 and 2 months after treatment (H, I). Primary errors did not differ (K, L).
Data information: Animal numbers: (A) and (D)
n = 9; (B, C, E, F)
n = 8; for AAV‐ΔGFP in (C) and (F)
n = 5, because 3 mice had to be excluded from evaluation due to accelerating seizure activity and resulting weight loss; (G–L)
n = 7; data represent mean ± standard error of 3 training sessions per day. **
P < 0.01; *
P < 0.05 by two‐way ANOVA for repeated measurements depicting only difference between treatments. Besides the differences between treatments, significance of the factor time (i.e., the training days) was observed for data depicted in (A) (
P = 0.0002); (B) (
P = 0.0009); (D) (
P < 0.0001); (E) (
P = 0.0010); and (F) (
P = 0.0212) suggestive of learning.