Figure 4. Schematics of electron transport chain (ETC).
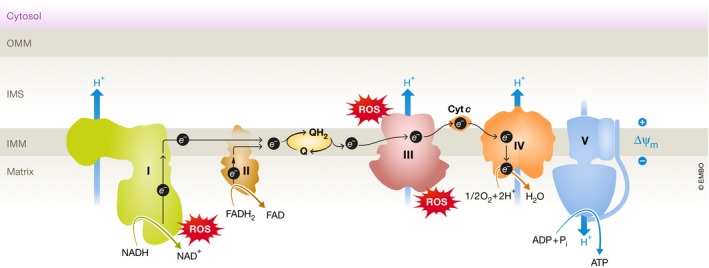
The ETC passes electrons from NADH and FADH 2 to protein complexes (I to V) and mobile electron carriers coenzyme Q (CoQ) and cytochrome c (Cyt c). Oxygen (O2) is the final electron recipient. The transfer of electrons generates energy to pump protons (H+) from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space. An electrochemical proton gradient is created across the inner mitochondrial membrane, allowing the protons to pass through complex V (ATP synthase) to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Complex I, NADH coenzyme Q reductase, complex II, succinate dehydrogenase, complex III, cytochrome bc 1 complex, complex IV, cytochrome c oxidase. Complex I and complex III are the main sites for superoxide (ROS) formation.
