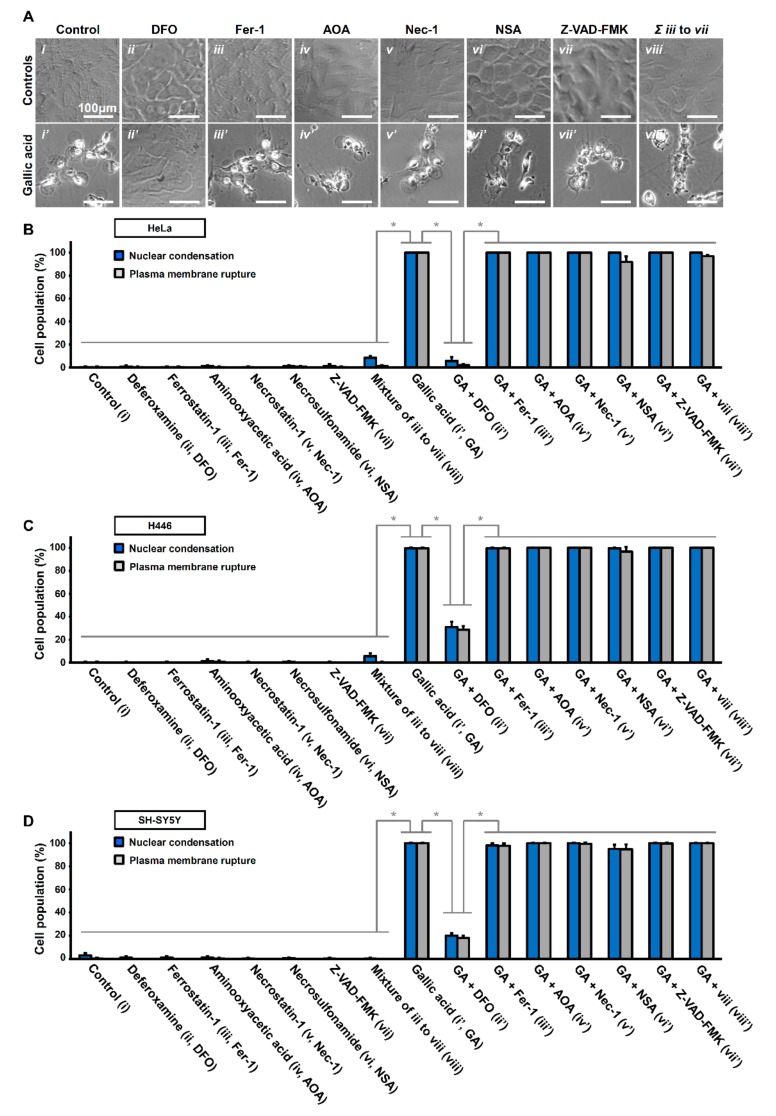
Figure 4.
Iron chelator deferoxamine suppresses gallic acid-induced cell death. (A) Representing confocal images of HeLa cells treated with (i) medium alone (Control), (ii) deferoxamine (DFO, 200 µM), (iii) ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1, 2 µM), (iv) aminooxyacetic acid (AOA, 2 mM), v) necrostatin-1 (Nec-1, 40 µM), (vi) necrosulfonamide (NSA, 5 µM), (vii) Z-VAD-FMK (50 µM), and (viii) co-treated with Fer1, AOA, Nec-1, NSA, and Z-VAD-FMK, with (lower panels, (i’–ix’)) or without (upper panels,(i–ix)) co-treatment of gallic acid (50 µg/mL) for 36 h. Cell morphology was observed by DIC microscopy. (B–D) Quantification of the cell death events in HeLa cells after gallic acid induction (50 µg/mL) with or without co-treatment with inhibitors with the conditions listed at the panel A for 36 h. The percentage in the population of HeLa cells displayed nuclear condensation (blue) and plasma membrane rupture (grey) as mentioned above in HeLa (B), H446 (C), and SY-SY5Y (D) cells. (Mean ± s.d.; n = 3; * p < 0.001).