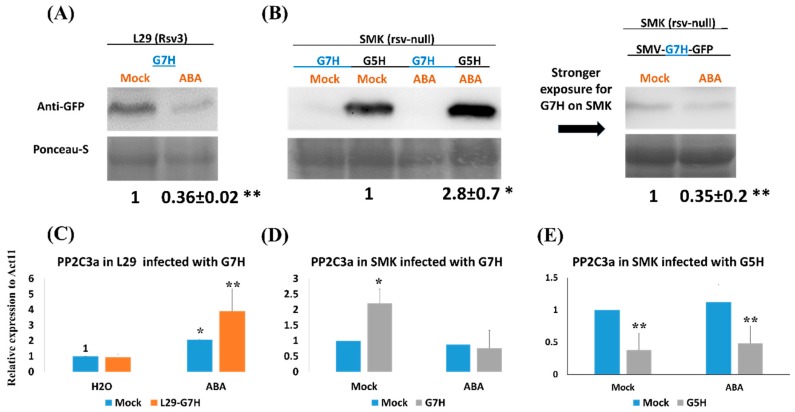
Figure 1.
Effect of abscisic acid (ABA) treatment on the accumulation of soybean mosaic virus (SMV) strains and on PP2C3a expression in L29 and Somyungkong (SMK) soybean cultivars. Protein blots of the soybean mosaic virus (SMV) in response to exogenous application of ABA (100 μM) or Mock (0.1 % MeOH) in: (A) L29 cultivar (carries the Rsv3 resistance gene) infected with the virulent strain G7H, or (B) SMK cultivar (rsv3-null) infected with G7H or the avirulent strain G5H (both strains express GFP). The upper panel shows the GFP level, and the lower panel shows Ponceau-S, which was used as a loading control. Relative expression levels of PP2C3a using RT-qPCR in response to G7H infection in L29 plants (C), G7H infection in SMK plants (D), and G5H plants (E). Actin11 was used as the internal control. Plants were sampled at 5 dpi. For (C–E), values are means standard deviation (SD) of three biological replicates. In each panel, values were compared to that of the mock-treated, uninfected plants (the bar on the left) with one-sided Student’s t-tests; * and ** indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05 and <0.01, respectively.