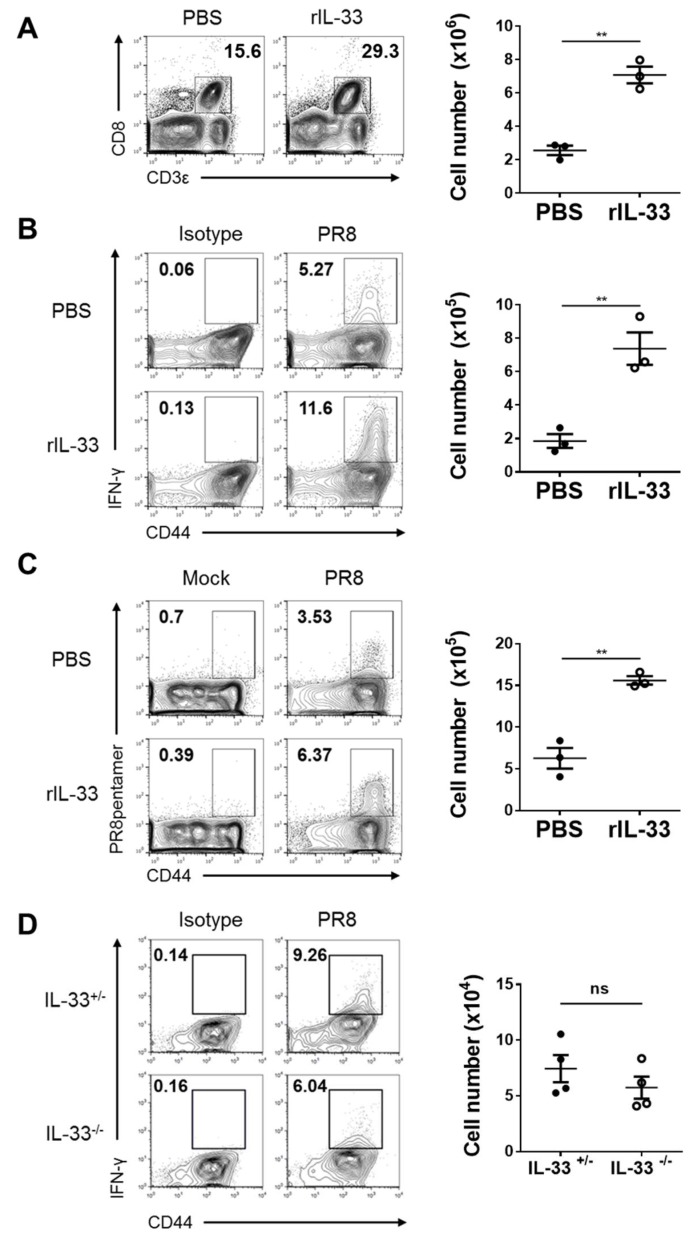
Figure 4.
Exogenous IL-33, but not endogenous IL-33, enhanced CD8 T-cell responses against influenza infection. (A–C) C57BL/6 mice were injected intranasally with 0.5 μg of rIL-33 or PBS daily for five days and infected with 50 PFU of PR8 influenza virus. (A) On day seven post-infection, the recruitment of CD3ε+ CD8+ T-cells to lungs was assessed by flow cytometry. (B) IFN-γ production by CD3ε+ CD8+ CD44hi T-cells post-stimulation with NP366–374 peptide was measured by intracellular staining. (C) NP366-374 antigen-specific CD3ε+ CD8+ CD44+ T-cells were measured by pentamer staining. (D) IL-33+/− and IL-33−/− mice were infected with 50 PFU of PR8 influenza virus. On day seven post-infection, IFN-γ production by CD3ε+ CD8+ CD44hi T-cells post-stimulation with NP366-374 peptide was measured by intracellular staining. ** p < 0.01; ns, not significant.