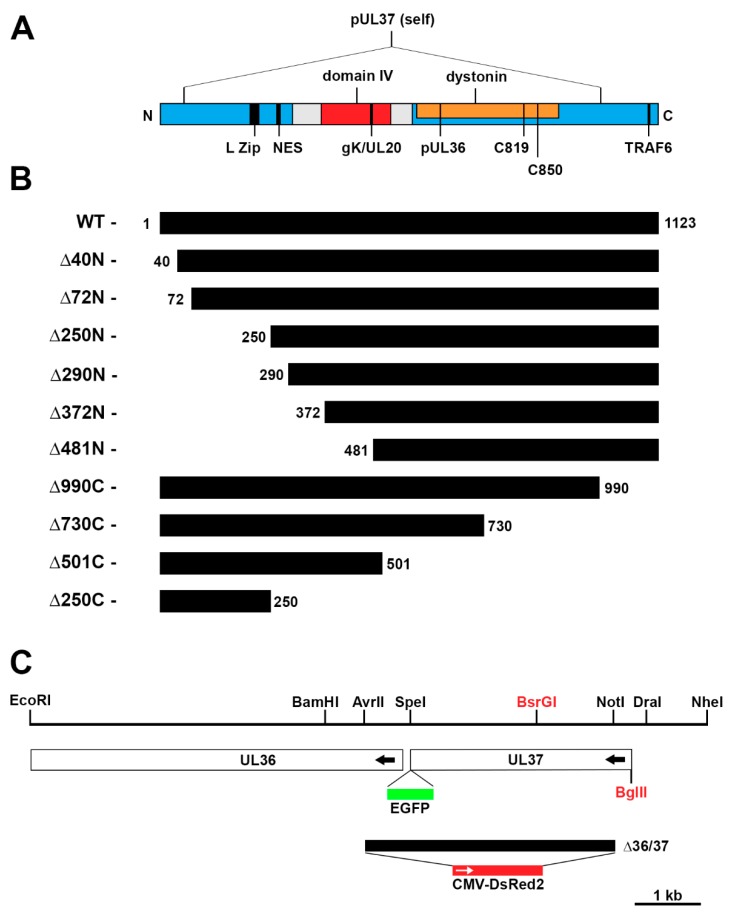
Figure 1.
Functional and interaction domains of the HSV-1 pUL37. (A) The carton illustrates the 1123 amino acid linear pUL37 polypeptide. The motifs identified to act as a nuclear export signal (NES), a leucine zipper (L Zip), deamidase active sites (C819 and C850), and the virulence R2 residues in domain IV (red) are shown, as well as the self (blue), pUL36, gK/pUL20 (474–480), dystonin (orange), and TRAF6 interaction domains [38,45,66,67,71]. (B) Polypeptide truncations of the N- and C-terminus of pUL37 were generated molecularly and transferred into the HSV-1 genome using marker-rescue/marker-transfer methods. Mutant polypeptides expressed a C-terminal EGFP fusion. (C) Carton of the UL37 and UL36 genetic locus of HSV-1. The figure shows the restriction enzyme fragments used to clone different regions of UL37 and to engineer mutant genes. These include the site of the insertion of EGFP ORF and the region of a UL36–UL37 double deletion followed by insertion of the CMV-DsRed2 cassette. Engineered restriction enzyme sites are shown in red.