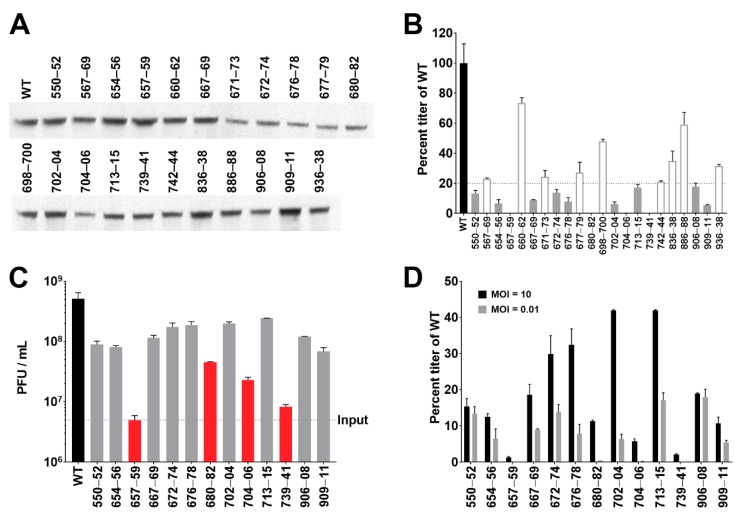
Figure 5.
Alanine scanning mutagenesis of conserved amino acids in the C-terminus of pUL37 reveals residues important for productive replication. (A) Lysates from Vero cells infected with 22 triple alanine scanning mutants of UL37–EGFP and wild-type (WT) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, as described in the legend of Figure 2, and the blot of the transferred proteins probed with anti-GFP rabbit antibodies to examine mutant pUL37–EGFP fusion expression. (B) Mutant viruses were analyzed for growth on Vero cells following infection of at MOI = 0.01 PFU/cell and titration of the virus burst 3 days post-infection, as described in the legend of Figure 2. Viruses with titers below 20% of WT are shaded grey, and those above 20% open bars. (C) The 13 viruses with most reduced titers in a multi-step growth curve were also analyzed for single-step growth by infection at MOI = 10 PFU/cell and harvested 24 h post-infection, as described in the legend of Figure 2. The data for the four most deleterious AAA mutants in the virus are shown as red bars. (D) Titers from the 13 viruses analyzed by both single- and multi-step growth are plotted as percent titer of WT for each corresponding experiment. All data represent the mean of at least two independent replicates with error bars of one standard deviation.