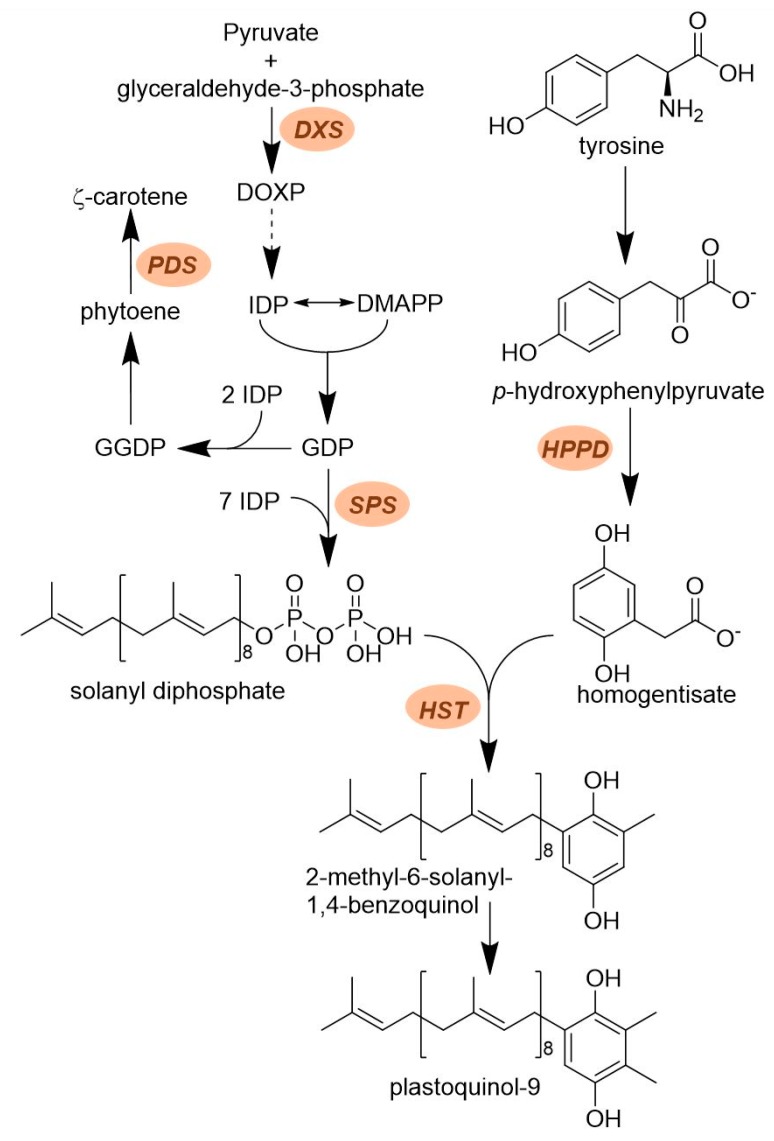
Figure 2.
Overview of the relationship between carotenoid and prenyl quinone biosynthesis. Biosynthesis of carotenoids and plastoquinone requires the MEP, terpenoid and homogentisate pathways. Older chemistry such as clomazone inhibits 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS), the first step in the MEP pathway; a number of chemical classes inhibit carotenoid biosynthesis by targeting phytoene desaturase (PDS); the newer triketone herbicides inhibit p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) involved in homogentisate biosynthesis. The two newest target sites affect solanyl diphosphate synthase (SPS) responsible for the synthesis of the terpenoid tail of plastoquinone or homogentisate solanesyl transferase (HST), the enzyme combining solanyl diphosphate and homogentisate to form a plastoquinone precursor.