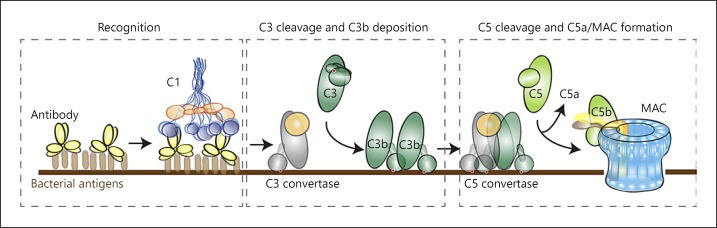
Fig. 2.
The complement reaction. Recognition of bacterial cells occurs via soluble pattern-recognition molecules (lectin pathway) or antibodies (classical pathway). Antibody-mediated complement activation is depicted here. C1 binds to antibodies on the surface and triggers formation of a C3 convertase enzyme that converts C3 into C3b. At high C3b densities on the surface, the C3 convertase switches substrate, from C3 to C5, and is now called a C5 convertase. C5 convertases convert C5 into the chemoattractant C5a and C5b that trigger formation of the MAC (C5b-9).