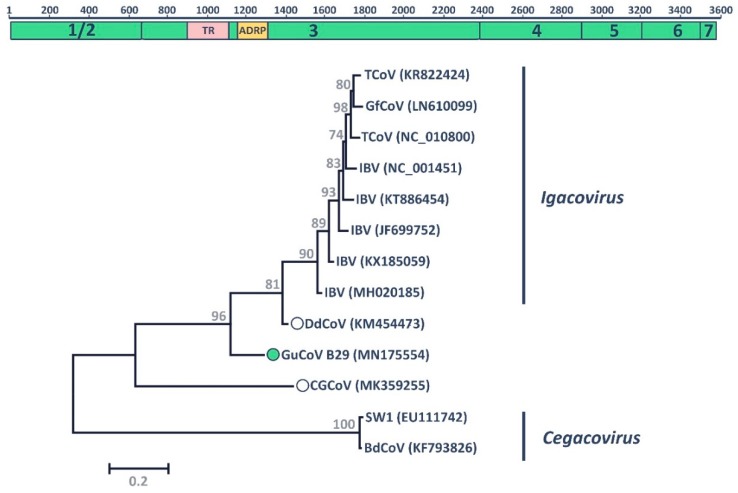
Figure 2.
Molecular characteristics of GuCoV B29. The organization of the partial 1a polyprotein of the novel virus is depicted at the top. Identified mature peptides (non-structural proteins, nsp1/2–7) are illustrated by green rectangles. The pink rectangle indicates the area in nsp3 where the tandem repeat (TR) was identified, while the yellow rectangle shows the location of the conserved ADP-ribose 1-“phosphatase (ADRP) replicase domain within nsp3. The scale bar on top represents the amino acid position within the polyprotein. The phylogenetic placement of GuCoV B29 within the genus Gammacoronavirus based on the concatenated alignments of the ADRP and 3C-like proteinase (3CLpro) (corresponding to nsp5) is shown at the bottom. The two species Igacovirus and Cegacovirus are indicated on the right. Accession numbers of sequences used (SW1: Beluga whale coronavirus; BdCoV: Bottlenose dolphin coronavirus; IBV: Infectious bronchitis virus; TCoV: Turkey coronavirus; GfCoV: Guinea fowl coronavirus; DdCoV: Dominant-duck coronavirus; GuCoV: Gull coronavirus; CGCoV: Canada goose coronavirus) are indicated in parentheses. Recently identified viruses that lack official taxonomic designations are indicated by circles with the virus identified in this study indicated by the filled green circle. The tree was built with the maximum likelihood method [47] using MEGA 7 [43] based on the Le Gascuel model [50], identified as the best-fitting model by the model test in MEGA. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites, branch lengths are proportional to genetic distances as indicated by the scale bar, and the outcome of the bootstrap analysis [48] is shown next to the nodes.