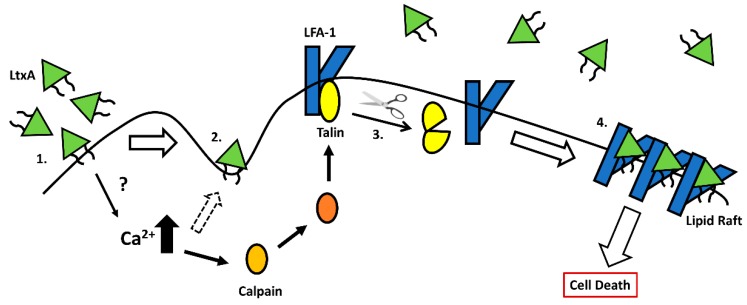
Figure 1.
Model for LtxA association with host cell membranes. 1. LtxA (shown with fatty acyl chains) passively adsorbs onto cell membranes and anchors via the fatty acylation. This is believed to elevate intracellular calcium levels. 2. Association of LtxA with the target cell membranes results in lipid bilayer destabilization, demonstrated by the formation of cell surface depression. 3. The elevated calcium levels activate the calcium-dependent protease calpain. Calpain cleaves talin, a cytoskeletal tethering protein that holds LFA-1 in place in the cell membrane. 4. LFA-1 can cluster in the lipid raft compartment where LtxA interaction with LFA-1 is mediated by the fatty acyl chains at the membrane interface, allowing for the toxin to become partially embedded into the cell membrane. Downstream signaling results in cell death.