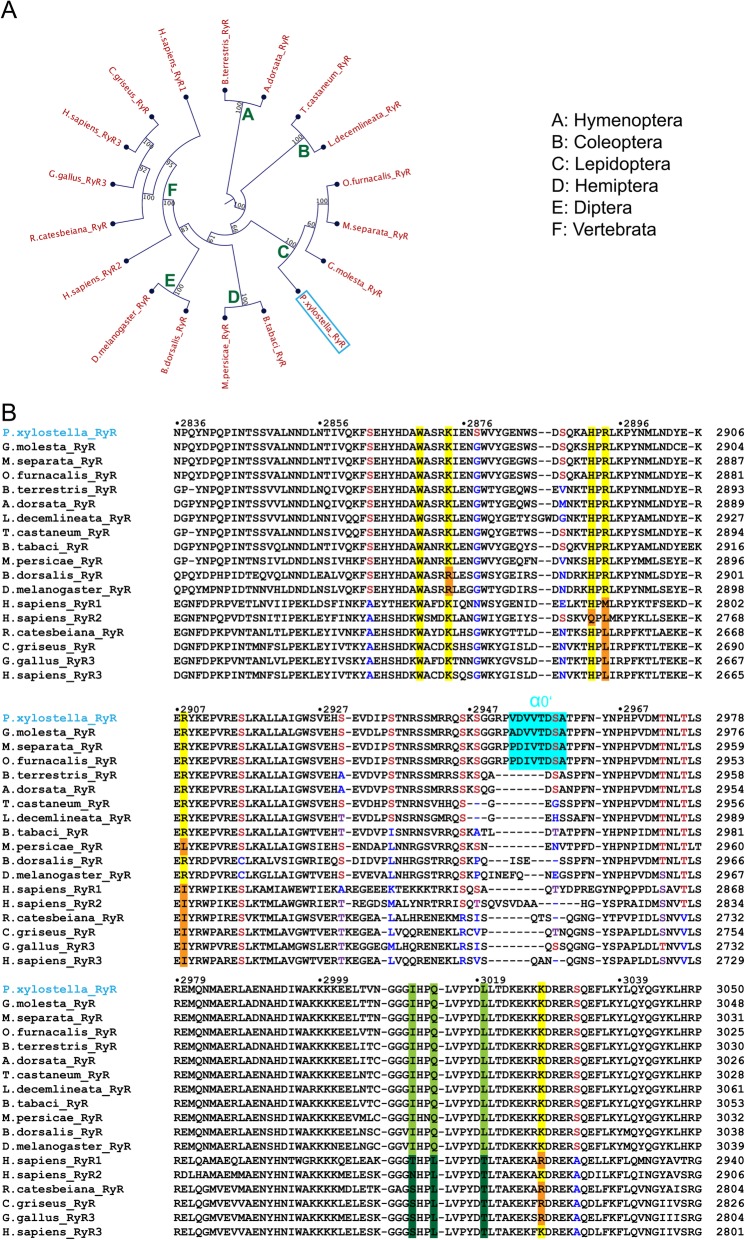
Fig. 9.
Phylogenetic analysis and sequence alignment. a Phylogenetic analysis of RyRs from different species, including Lepidoptera (Plutella xylostella: NP_001296002.1, Grapholitha molesta: ALM96708.1, Mythimna separate: AWV67093.1, Ostrinia furnacalis: AGH68757.1), Hymenoptera (Bombus terrestris: XP_012175583.1, Apis dorsata: XP_006622367.1), Coleptera (Leptinotarsa decemlineata: AHW99830.1, Tribolium castaneum: NP_001308588.1), Hemiptera (Bemisia tabaci: AFK84957.1, Myzus persicae: XP_022160123.1), Diptera (Bactrocera dorsalis: AHY02115.1, Drosophila melanogaster: NP_001246211.1), and vertebrate (Homo sapiens1: NP_000531.2, Homo sapiens2: NP_001026.2, Rana catesbeiana: BAA04647.2, Cricetulus griseus: ERE72086.1, Gallus gallus: NP_996757.2, Homo sapiens3: NP_001027.3). b Sequence alignment of RyRs from different species (same as in panel A). The phosphorylation sites are colored in red (conserved), purple (semi-conserved), or blue (non-conserved); the glycerol-coordinating residues are highlighted in yellow (conserved) or orange (non-conserved); the insect-specific HD1-interacting residues are highlighted in light green (conserved) or dark green (non-conserved); the Lepidoptera-specific helix α0′ is highlighted in cyan