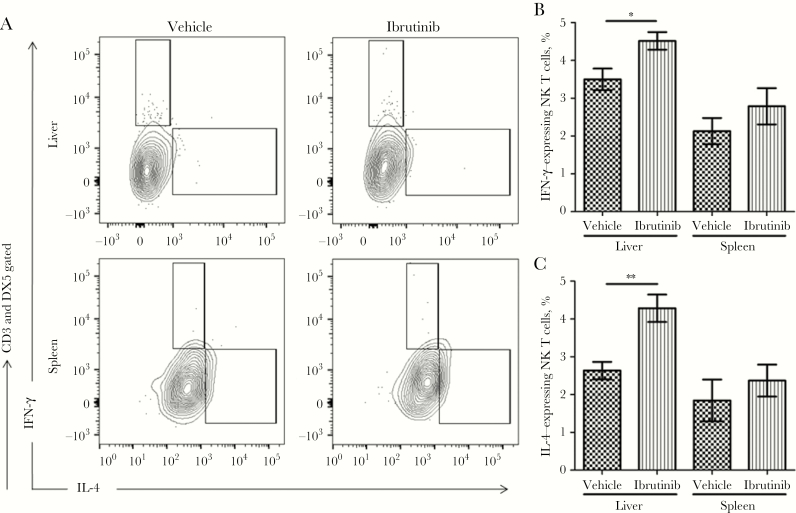
Figure 5.
Ibrutinib treatment increases interferon γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin 4 (IL-4) production in natural killer (NK) T cells. The livers and spleens of the ibrutinib-treated and vehicle-treated groups were harvested and analyzed for cell populations responsible for the production of IFN-γ and IL-4. A, Intracellular detection of IFN-γ and IL-4 by flow cytometry after 14 days of ibrutinib treatment. Single-cell suspensions were prepared from livers and spleens and stimulated with PMA (20 ng/mL) plus ionomycin (1 μg/mL) in the presence of brefeldin for at least 6 hours. Cells were gated for CD3 and DX5 and then evaluated for IFN-γ and IL-4 production. B, Percentage of IFN-γ–expressing NK T cells among CD3+DX5+ gated cells. C, Percentage of IL-4–expressing NK T cells among CD3+DX5+ gated cells. Data are representative of one of the 3 independent experiments, with 5 mice/group. *P < .05 and **P < .01, by the unpaired t test.