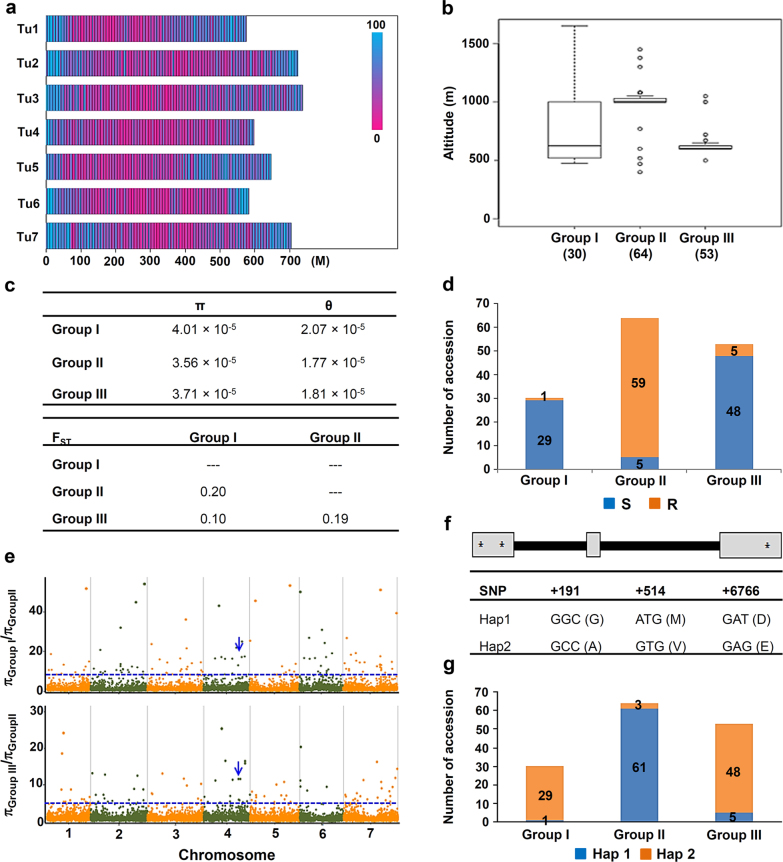
Extended Data Fig. 9. Population analysis.
a, Distribution of transcriptomic-based SNPs on the seven DNA pseudomolecules (Tu1–Tu7) of T. urartu. The SNPs were calculated using a 1-Mb window. b, Boxplot comparison of altitude ranges of Tu accessions. The number of accessions in each group is indicated in parentheses. The line inside each box represents the median, the ends of each box define the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the error bars mark the 10th and 90th percentiles. Outliers are displayed as open circles. c, Analysis of genetic diversity and differentiation. The π, θ and FST values were estimated for the three groups of Tu accessions using transcriptomic SNPs. d, Reaction phenotypes of Tu accessions to the wheat powdery mildew fungus Bgt. Most of the accessions in Groups I and III (96.7% and 90.6%, respectively) were susceptible to Bgt (race E09), whereas the majority of Group II accessions (92.2%) showed resistance. e, A total of 141 (top 1%; πGroup I/πGroup II > 7.7) and 143 (top 1%; πGroup III/πGroup II > 4.3) signals were considered to be candidate sweeps (dots above the dashed horizontal threshold line). The Tu accessions in Groups I, II and III were 30, 64 and 53, respectively. Blue arrows indicate the wall-associated receptor protein kinase gene (TuWAK, TuG1812G0400002796), whose haplotype variations showed strong associations with resistance or susceptibility to Bgt. f, Exon (box)–intron (line) structure of TuWAK and its two major haplotypes (Hap1 and Hap2). The positions of the three SNPs that differ between Hap1 and Hap2 are shown. Amino acid changes caused by these SNPs are also displayed. g, Distribution of Hap1 and Hap2 in the three groups of T. urartu accessions. Hap1 was the major haplotype in Group II, which was strongly associated with resistance to Bgt, while Hap2 was the main haplotype in Groups I and III, and associated with susceptibility to Bgt. In d and g, the accessions in each group were further sorted based on the response to powdery mildew infection (d) or the possession of TuWAK haplotypes (g), with the assorted accession numbers indicated in appropriate columns.