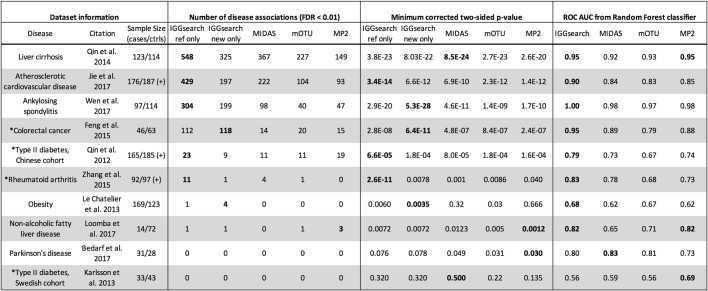
Extended Data Table 1.
Metagenome-wide disease associations using IGGsearch and other tools
IGGsearch and three other tools—MIDAS, mOTU and MetaPhlAn2 (abbreviated as MP2)—were used to estimate the abundance of species across samples that span ten studies. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to identify differentially abundant species and P values were corrected for multiple hypothesis testing using the false discovery rate procedure. For IGGsearch, disease associations are split into ‘ref only’ (species-level OTUs with reference genomes) and ‘new only’ (species-level OTUs with only MAGs). Additionally, species profiles from all four tools were used to train random-forest machine learning classifiers to predict disease state. Optimized models were identified by testing 1,000 random forests with random combinations of model parameters, and choosing the model with the greatest ROC AUC. To avoid overfitting, tenfold cross-validation was performed. Reported AUC values are averages across 100 random forest runs. Bold text indicates the tool that performed best for each disease; asterisks indicates studies used for MAG recovery. (+), studies in which a subset of cases was excluded owing to medication for disease treatment.