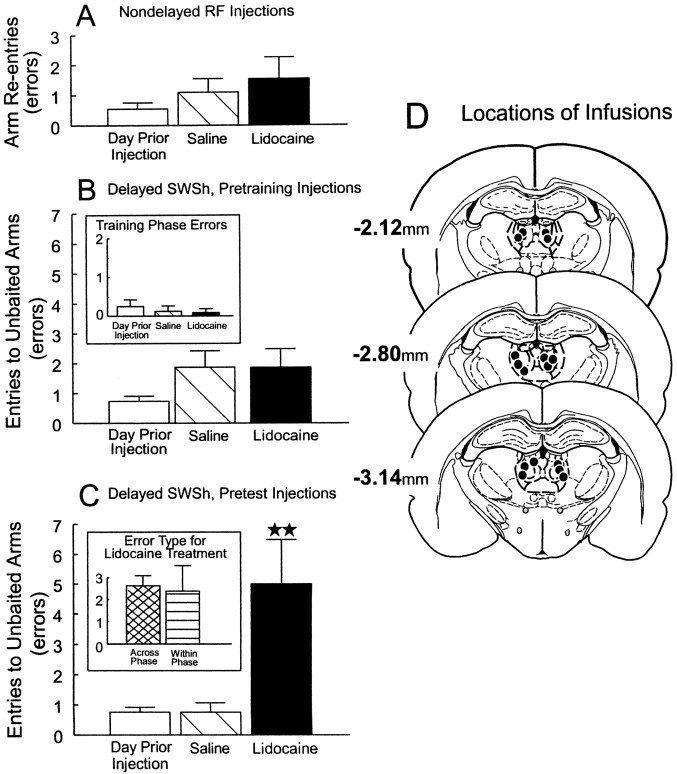
Fig. 1.
Effects of bilateral inactivation of the MDNt on performance of delayed and nondelayed radial arm maze tasks.A, Number of errors (mean ± SEM) made by rats on the day before the first injection (open bar) and after infusions of saline (hatched bar) or lidocaine (black bar) into the MDNt before the nondelayed RF task.B, Number of errors (mean ± SEM) made by rats during the test phase on the day before the first injection (open bar) and after infusions of saline (hatched bar) or lidocaine (black bar) into the MDNt before the training phase of the delayed SWSh task.Inset, Number of errors made during the training phase on the day before the first injection (open bar) and on saline (hatched bar) and lidocaine (black bar) injection days. C, Number of errors (mean ± SEM) made by rats during the test phase on the day before the first injection (open bar) and after infusions of saline (hatched bar) or lidocaine (black bar) into the MDNt before the test phase of the delayed SWSh task. ★★Significance at p < 0.001 relative to saline and previous day. Inset, Number of across-phase errors (cross-hatched bar) and within-phase errors (striped bar) made by rats on lidocaine injection days. D, Location of infusions (black circles) for all rats with acceptable placements receiving infusions into the MDNt before the test phase of the delayed SWSh task. Plates are computer-generated adaptations from Paxinos and Watson (1986). Numbers beside each slide correspond to millimeters from bregma.