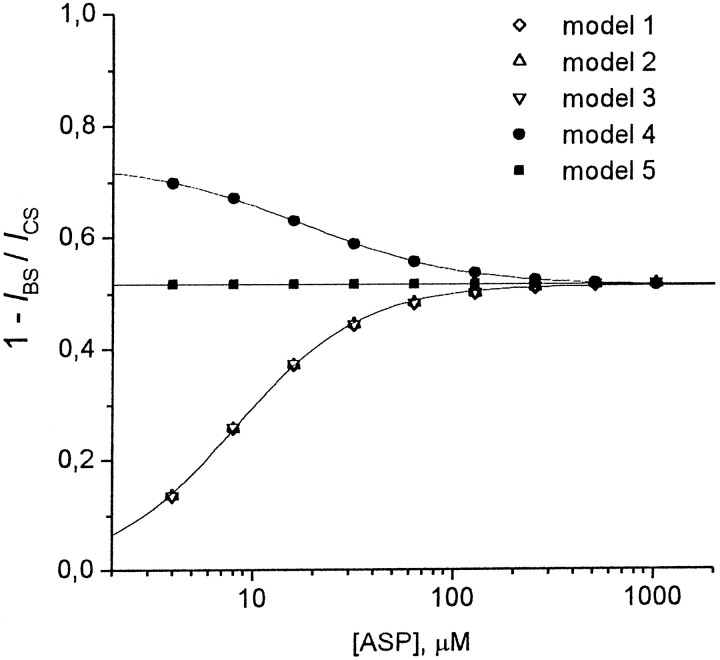
Fig. 9.
Agonist dependencies of the stationary current inhibition predicted by models 1–5. The degree of the stationary current inhibition, 1 −IBS/ICS, rises with the agonist concentration for models 1–3, decreases for model 4, and is constant for model 5. The agonist dependencies predicted by models 1, 2, and 3 coincided at [B] = 28, 2.6, and 1.1Kd, respectively, and were well fitted with Equation 2 (solid line). The values of the fitting parameters were as follows: A1= 0, A2 = 0.515 ± 0.002, [A]0 = 8.18 ± 0.15 μm, andnHill = 1.39 ± 0.04. The fitting of the agonist dependence predicted by model 4 at [B] = 2.5Kd (solid line) gave the following values of the fitting parameters:A1 = 0.733 ± 0.003,A2 = 0.515 ± 0.001, [A]0 = 17.9 ± 0.6 μm, andnHill = 1.13 ± 0.03. The degree of the stationary current inhibition for model 5 did not depend on the agonist concentration and was equal to 0.515 at [B] = 1.1Kd. The values of parameters were as follows: P0 = 0.09,τwash = 30 msec, andk2 = 1000 sec−1.