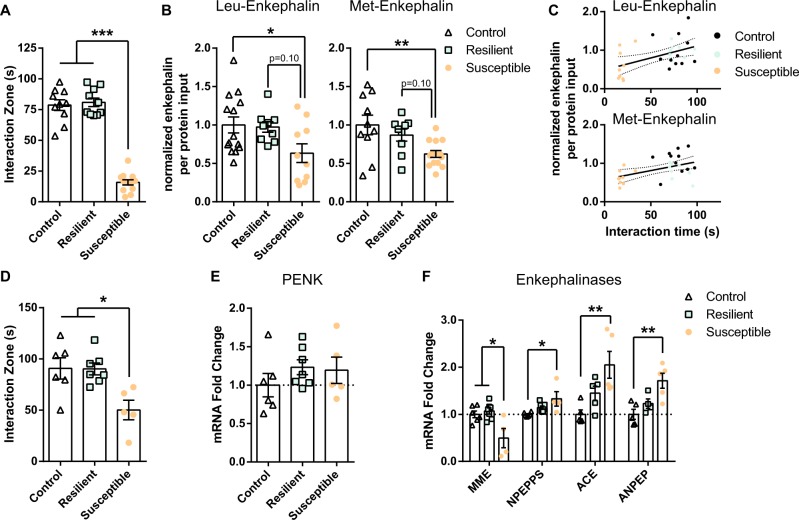
Fig. 1.
Enkephalin levels are decreased in the NAc of mice susceptible to CSDS. Transcription of enkephalin precursor proenkephalin is not altered, while enzymes that degrade enkephalins are reduced in CSDS-susceptible mice. a Social interaction scores from the animals used in enkephalin RIA experiment (***p < 0.001, post-hoc; one-way ANOVA: p < 0.001). b CSDS-susceptible mice display decreased Leu- (*p < 0.05, post-hoc; one-way ANOVA: p < 0.05) and Met-enkephalin levels (**p < 0.01, post-hoc; one-way ANOVA: p < 0.01) in the NAc compared to the non-defeated controls. c Leu- (p < 0.05, R2 = 0.21) and Met-enkephalin levels (p < 0.05, R2 = 0.21) within the NAc correlates with the social interaction scores. d Social interaction scores from the animals used in NAc qRT-PCR experiment (*p < 0.05, post-hoc; one-way ANOVA: p < 0.01). e NAc mRNA levels of proenkephalin (PENK) are not reduced in susceptible animals compared to the controls. f Increased mRNA levels of NPEPPS, ACE, ANPEP, and a decrease in MME were observed in susceptible animals (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, post hoc; one-way ANOVA: p < 0.05)