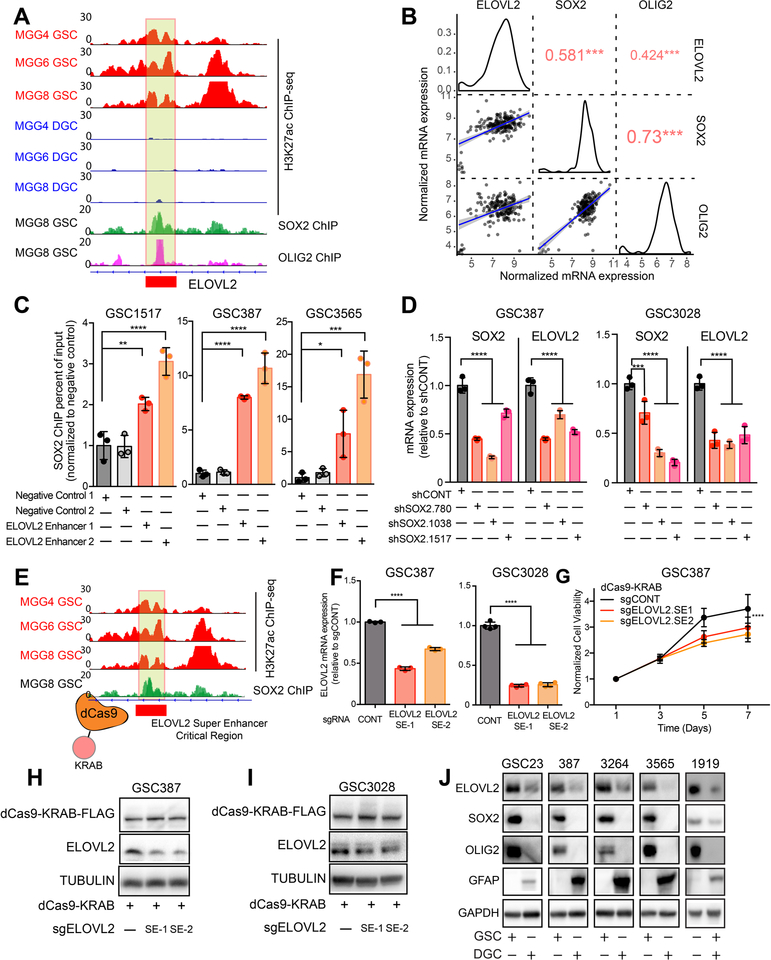
Figure 3. The ELOVL2 glioblastoma stem cell super-enhancer is driven by SOX2 and is necessary for maintenance of high ELOVL2 expression.
(A) H3K27ac signal at the ELOVL2 super-enhancer locus in three matched GSCs and DGCs (MGG4, MGG6, and MGG8). SOX2 and OLIG2 ChIP-seq data is shown at the same locus in the MGG8 model. Box indicates putative super-enhancer critical region with SOX2 binding site. Data was derived from (26).
(B) Correlation between ELOVL2, SOX2, and OLIG2 in the TCGA HG-U133A glioblastoma dataset restricted to the classical subtype. Red numbers indicate the correlation R value, *** p < 0.001.
(C) Enrichment of SOX2 binding over input by ChIP-qPCR in two negative control regions compared with two primers against the ELOVL2 super-enhancer region as demonstrated in (A). Three technical replicates were used for each condition. Statistical significance was assessed using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple test correction. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.
(D) qPCR analysis of mRNA expression of SOX2 and ELOVL2 following knockdown with three independent, non-overlapping shRNAs targeting SOX2 (shSOX2.780, shSOX2.1038, shSOX2.1517) or a non-targeting shRNA (shCONT). Three technical replicates were used for each condition. Statistical significance was assessed using a two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple test correction, ****, p < 0.0001.
(E) Schematic showing targeting of the ELOVL2 Super-enhancer critical region using a catalytically-dead dCas9 fused to a transcriptional repressor domain (KRAB).
(F) qPCR analysis of ELOVL2 mRNA expression in GSC387 and GSC3028 cells following treatment with dCas9-KRAB and two sgRNAs targeting the ELOVL2 super-enhancer critical region or an empty dCas9-KRAB vector. Three technical replicates were used for each condition. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, ****, p < 0.0001.
(G) Cell viability in the GSC387 cell model over a 7-day time course following treatment with dCas9-KRAB and two sgRNAs targeting the ELOVL2 super-enhancer critical region or an empty dCas9-KRAB vector. 6 technical replicates were performed for each group. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple hypothesis test correction (****, p < 0.0001).
(H) Western blot of ELOVL2 protein levels in GSC387 cells following treatment with dCas9-KRAB and two sgRNAs targeting the ELOVL2 super-enhancer critical region or an empty dCas9-KRAB vector. FLAG antibody was used to detect presence of the dCas9 protein.
(I) Same as (H) for GSC3028 cells.
(J) Western blot analysis of ELOVL2 protein levels in five GSCs and matched DGCs. SOX2 and OLIG2 were used to mark GSCs, while GFAP marked DGCs. GAPDH was used as a loading control.