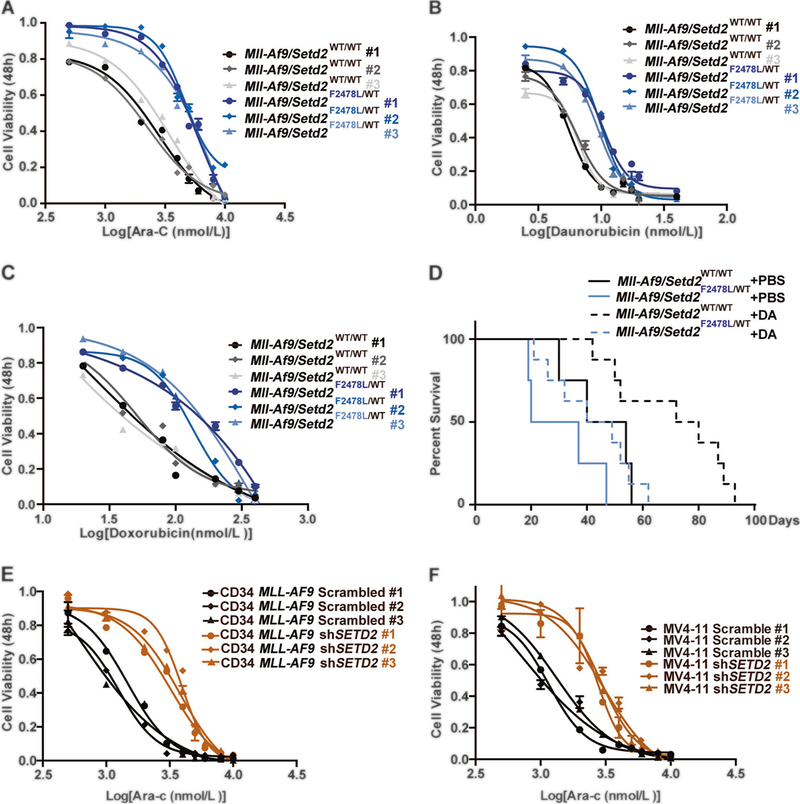
Fig. 3.
Setd2 mutation leads to chemoresistance of Mll-Af9 AML cells. a–c Drug resistance assays in multiple clones from different individuals of both Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/Setd2F2478L/WT primary bone marrow leukemic populations treated with Ara-C (a), Daunorubicin (b), or Doxorubicin (c). Drug concentrations are indicated on the horizontal axis. Three biological replicates of each genotype are performed in triplicate and the data are presented as the mean ± SD values. d After transplantation of bone marrow cells from Mll-Af9 or Mll-Af9/ Setd2F2478L/WT mice to B6-SJL (CD45.1+) mice (n = 4 in each group, two independent biological replicates) for 3 weeks, the chemotherapy regimen was performed by intravenous (i.v.) injection of Doxorubicin and Ara-C. Days of survival of treated and nontreated mice in the Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/Setd2-mutant cohorts were recorded. e, f Drug resistance assays in Mll-Af9 human CD34+ cells (e) or the MV4–11 cell line (f) with shRNA-mediated SETD2 knockdown. Three biological replicates of each genotype are performed in triplicate, and the data are presented as the mean ± SD values