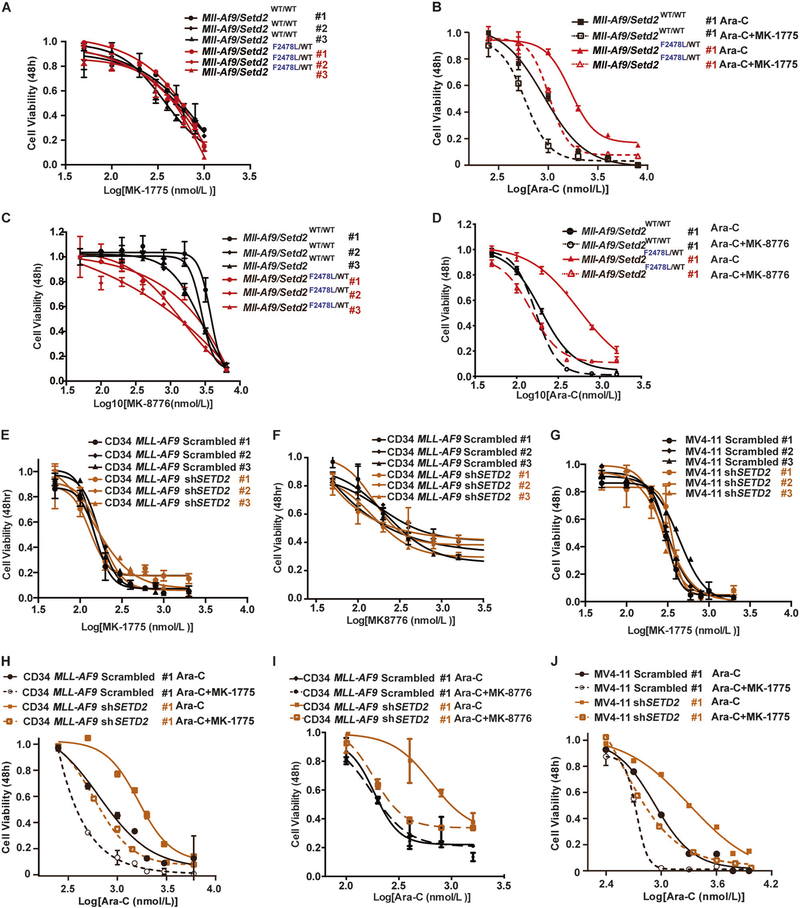
Fig. 5.
Checkpoint inhibition resensitizes resistant Mll-Af9/Setd2 double-mutant AML cells to chemotherapy. a Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/ Setd2F2478L/WT primary bone marrow leukemic cells were treated with variable concentrations of the WEE1 inhibitor MK-1775 for 48 h. b Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/Setd2F2478L/WT primary bone marrow leukemic cells were treated with variable concentrations of the combination of Ara-C and MK-1775 for 48 h. c Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/Setd2F2478L/WT primary cells were treated with variable concentrations of the CHK1 inhibitor MK-8776 for 48 h. d Mll-Af9 and Mll-Af9/Setd2F2478L/WT primary cells were treated with variable concentrations of the combination of Ara-C and MK-8776 for 48 h. e–g shRNA-mediated Setd2 knockdown was performed in MLL-AF9 human CD34+ cells (e, f) and the MV4–11 cell line (g). After puromycin selection, the stable cell lines were treated with variable concentrations of the WEE1 inhibitor MK-1775 (e, g) or CHK1 inhibitor MK-8776 (f). h MLL-AF9 human CD34+ Scrambled and shSETD2 cells tested in the combination of Ara-C and MK-1775 for 48 h. i MLL-AF9 human CD34+ Scrambled and shSETD2 cells tested with the combination of Ara-C and MK-8776 for 48 h. j MV4–11 Scrambled and shSETD2 cells tested with the combination of Ara-C and MK-1775 for 48 h. The data in (a, c, e, f, g) are shown as three biological replicates of each genotype performed in triplicate and presented as the mean ± SD values. The data in (b, d, h, i, j) are shown as the mean ± SD values (n = 3 technical replicates) of one independent clone