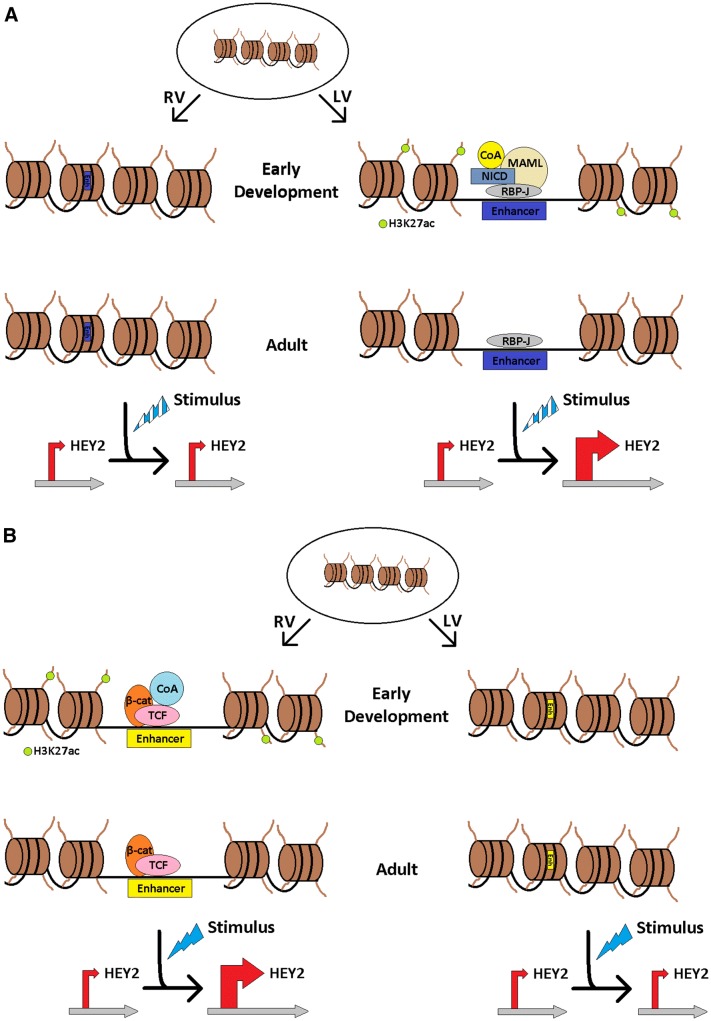
Fig. 1.
Schematic of chamber-specific “priming” and differential HEY2 expression levels. a Canonical Notch signaling regulates early cardiac development mediated by nuclear translocation of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD), forming a complex with the DNA-binding transcription factor RBP-J (recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region), MAML (mastermind-like protein), and other coactivators (CoA) to form the Mastermind-containing transcriptional complex at the enhancer region (blue). In the adult during homeostasis, RBP-J is bound to this blue enhancer element in the left ventricle (LV), but not the right ventricle (RV). Upon a pathologic stimulus that reactivates Notch signaling, expression of HEY2 is upregulated only in the “primed” LV, whereas there is no change in HEY2 expression levels in the RV. b Canonical Wnt signaling regulates early cardiac development that is mediated by nuclear translocation of β-catenin (β-cat) forming a complex with the DNA-binding T-cell factor (TCF) and other coactivators at a distinct HEY2 enhancer region (yellow). In the adult during homeostasis, β-catenin is bound to the yellow enhancer in the RV, but not the LV. In reciprocal fashion to Notch signaling, a stimulus that reactivates Wnt signaling results in HEY2 upregulation in the “primed” RV, but no change in HEY2 expression in the LV