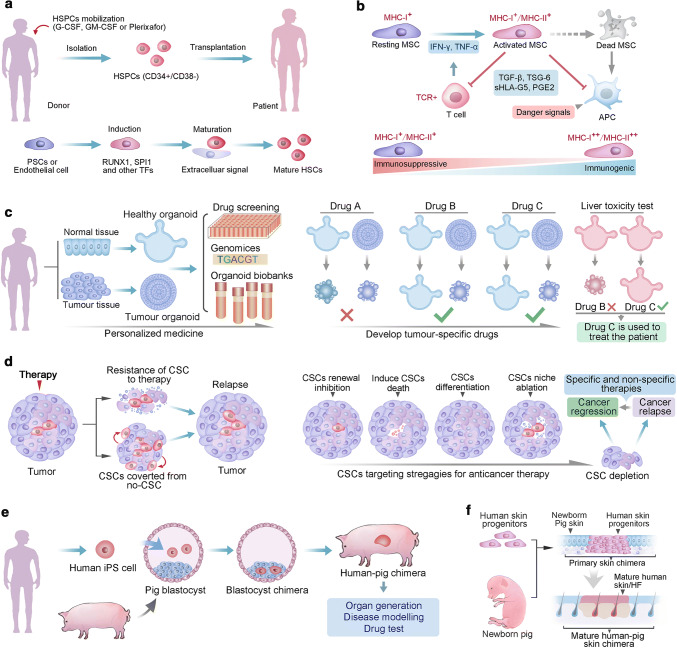
Fig. 5.
Stem cell application and perspectives. a Two distinct procedures to collect HSCs for transplantation. HSCs are isolated from donor blood cells, in which the HSCs are mobilized with G-CSF, GM-SCF or plerixafor, and enriched with HSCs marker of CD34+/CD38−. Alternatively, protocols have established to produce HSCs ether from endothelial cells, or from human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), these two protocols treated initiate cells with overlapping cocktails of transcription factors. The primary HSCs need to receive as-yet-unknown extracellular signals for further maturation. b MSC immunosuppressive capacity and immunogenicity are affected by levels of systemic or local inflammatory cytokines. High immunosuppressive potential of MSCs is achieved via suppression of T cell activation and inhibition of antigen-presenting cell (APC) maturation. Whereas, MSCs that do not tip the balance toward immunosuppression are prone to immunogenicity and result in immune detection and destruction, as debris from apoptotic MSCs are processed by APCs in the context of danger signals. The rate of immune detection of allogeneic MSCs is determined by the balance between relative expression of immunogenic and immunosuppressive factors in MSCs. IFN-γ, interferon gamma; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; sHLA-G5, soluble human leukocyte antigen-g5; TCR, T cell receptor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TSG-6; TNF-stimulated gene 6 protein. c Organoids generated from patient-derived healthy and tumor tissues can be genetically characterized and used for drug screening, and can be cryopreserved and stored in living organoid biobanks. Organoids developed from healthy tissue of the same patient can be used to screen drugs that are less toxic to healthy cells while selectively kill tumor cells. Moreover, hepatocyte organoid cultures may be used to test for hepatotoxicity. In this schematic example, drug C could specifically kills tumor organoids and does not show hepatotoxicity, and thus it seems most suitable for treating the patient. d CSC model of cancer relapse. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanism contribute to the CSCs resistance to the medical therapy, in addition, non-CSCs may convert to CSCs and replenish the CSCs pool, ether CSCs drug resistance or replenish result in cancer relapse. The CSC model suggests that inhibiting CSC self-renewal, inducing CSC specific cell death, inducing CSC differentiation or targeting CSC niche would lead to the depletion of the CSCs pool and subsequent tumor regression. Nevertheless, if the CSC is reversed from no-CSCs, further specific and no-specific therapies will be needed the for the final regression of tumor. e The principle of interspecies blastocyst complementation for the generation of human–animal chimaeras. Human PSC-derived organ could help to solve the severe shortage of organ donors. Additionally, Human–animal chimaeras could be useful for modeling human diseases and for testing the efficacy and safety of a candidate drug in vivo. f The principle of tissue complementation chimera. In this example, human-pig integumentary chimera was achieved via transplanting human skin progenitors to the skin incision of newborn pig. The engraftment of human progenitors will develop to mature human skin tissue with appendage organs, such as hair follicle