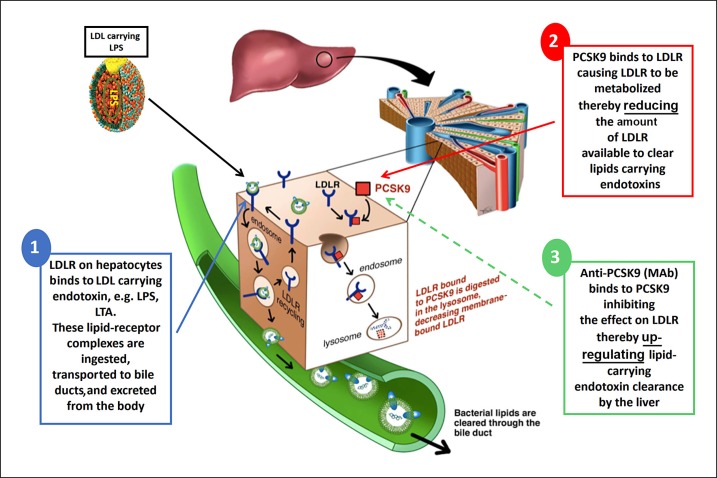
Fig. 2.
LPS clearance in the human host. (1) LPS from gram-negative bacteria carried within LDL particles binds to the LDLR on the surface of liver cells. The LPS-LDLR complex is then internalized, and while LDLR is recycled to the cell surface, LPS is cleared from the circulation through the bile duct. (2) When present, PCSK9 binds to LDLR on the cell surface and targets its lysosomal degradation. Therefore PCSK9, by preventing LDLR recycling, reduces the amount of LDLR available to clear LPS carried within LDL particles. (3) Anti-PCSK9 therapy (MAb) binds to PCSK9 and inhibits PCSK9-induced degradation of LDLR, upregulating the hepatic clearance of LPS carried within LDL. Adapted from [22]. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDLR, LDL receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; Ab, monoclonal antibody.