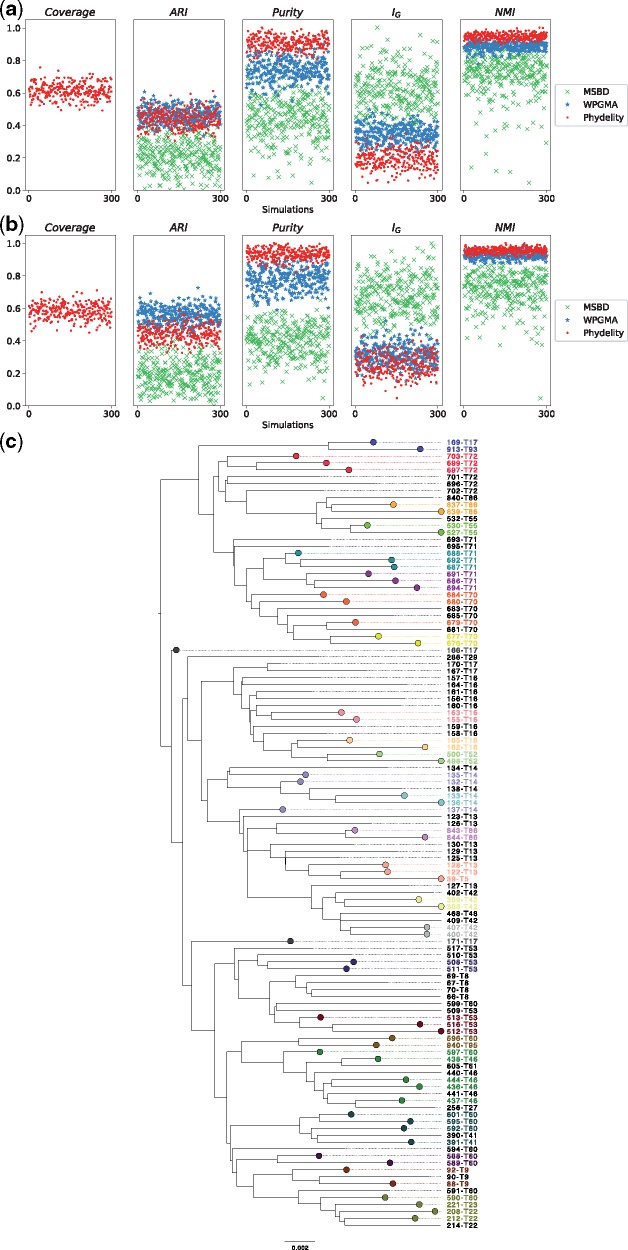
Figure 2.
Clustering results of simulated HIV epidemics in a hypothetical MSM sexual contact network. (a) Clustering metrics for clustering algorithms (Phydelity, weighted pair-group method of analysis (WPGMA) and multi-state birth−death (MSBD) methods) applied simulated phylogenies with inter-communities transmission rates weighted at half of within-community rates (i.e. w = 0.5). Coverage refers to the proportion of tips clustered by Phydelity. Adjusted rand index (ARI) measures how accurate the output clusters corresponded with the community labels. Purity gives the average extent clusters contain only a single class of community. Modified Gini index () is the probability that a randomly selected sequence would be incorrectly clustered. Normalised mutual information (NMI) accounts for the trade-off between clustering quality and number of clusters. (b) Results for simulations where inter-communities transmission rates were identical to within-community rates (i.e. w = 1.0). (c) Sample output clusters of Phydelity for a subtree of an example simulation (w = 0.5). Tips that were clustered by Phydelity are distinctly coloured according to their cluster membership. By relaxing the monophyletic assumption, Phydelity is capable of detecting paraphyletic clusters (e.g. transmission pair 166-T17 and 171-T17 and cluster subtending 132-T14, 135-T14 and 137-14).