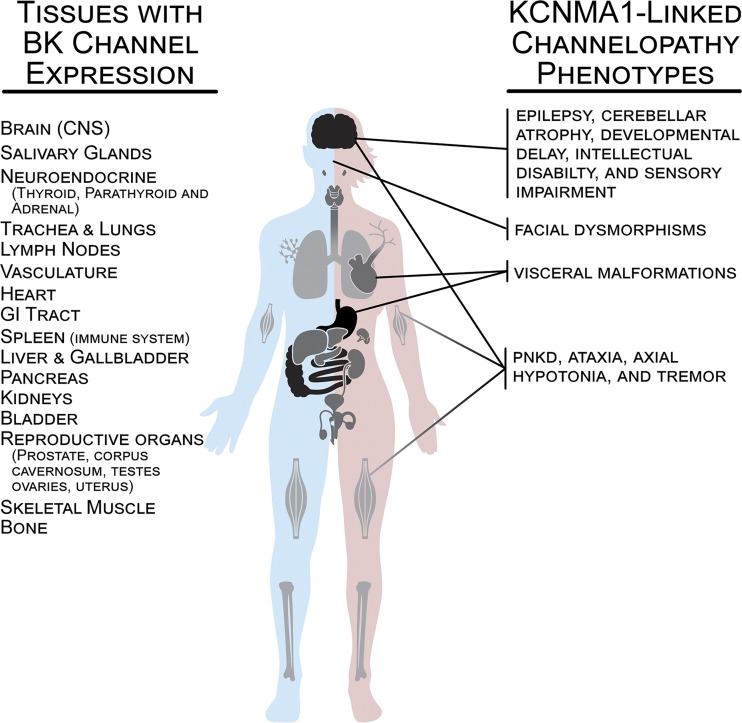
Figure 2.
BK channel expression in human tissues and prominent phenotypes reported in patients with KCNMA1-linked channelopathy. Major tissues or systems expressing BK channels are depicted in black (high relative expression), gray (medium), and light gray (low). Organs demonstrating high levels of BK channel expression include the CNS (olfactory system, neocortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, thalamus, habenula and its tract to the interpeduncular nucleus in the midbrain, cerebellum, vestibular nuclei in the hindbrain, and spinal cord), gastrointestinal tract (stomach, small intestine, and colon), and reproductive organs (corpus cavernosum, prostate, testes, ovaries, and uterus). Organs demonstrating medium BK channel expression include salivary glands, neuroendocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal), heart, urinary bladder, liver and gallbladder, kidneys, and spleen/immune system. Organs demonstrating low levels of BK channel include lungs, lymph nodes, vasculature, skeletal muscle, and bone. Data on expression levels were derived from the Human Protein Atlas v18.1 (https://www.proteinatlas.org; Uhlén et al., 2015), the NCBI Gene Database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), and published reports (Dworetzky et al., 1994; McCobb et al., 1995; Brenner et al., 2000).