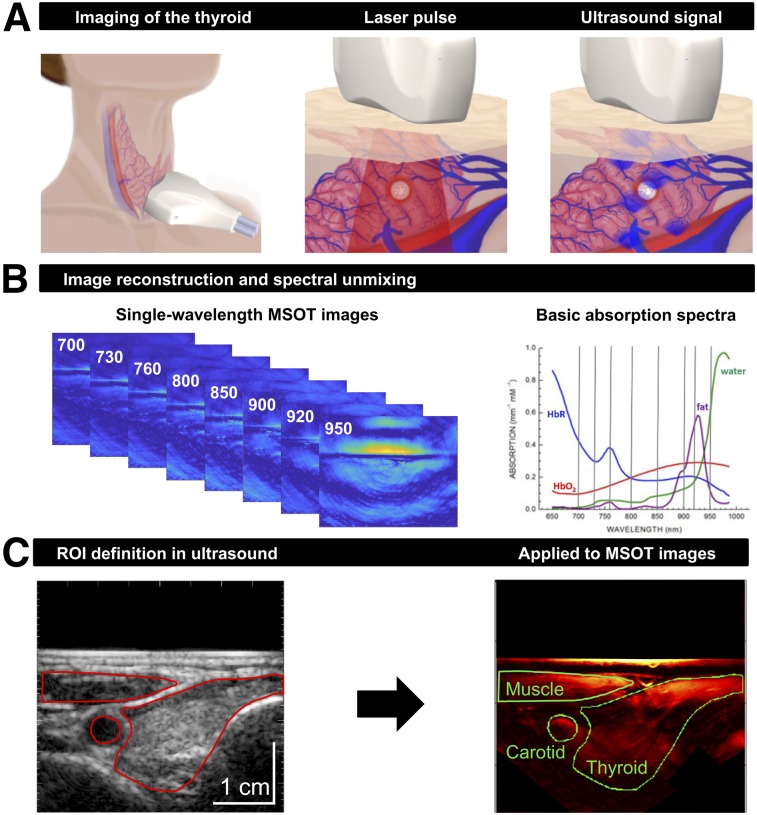
FIGURE 1.
Principles of clinical MSOT of thyroid. (A) Scheme of examination of thyroid gland with handheld hybrid MSOT/ultrasound system (left). Patients with thyroid nodules, healthy individuals, and Graves’ disease patients were scanned in a reproducible setup. Optoacoustic imaging is based on absorption of irradiated laser pulses within tissue (middle), followed by thermoelastic expansion and induction of ultrasound waves that can be detected with handheld detector (right). (B) In a first step, MSOT images are acquired for single wavelengths (left). Spectral unmixing, based on specific absorption spectra of different tissue constituents (right), allows assessment of functional parameters such as HbR, HbO2, fat content, and water content. (C) Transversal ultrasound image of thyroid gland and surrounding tissue allows exact localization of anatomic structures (left). ROIs drawn on ultrasound images were transferred to coregistered pseudo color-coded averaged MSOT images (here, HbT) for visual and quantitative analysis (right).