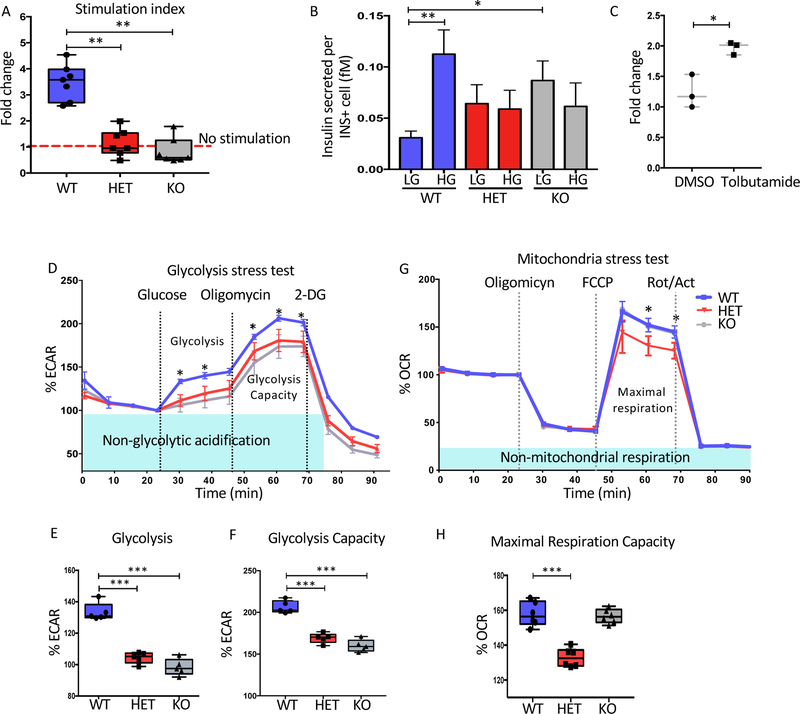
Figure 4: HNF1A is needed for optimal insulin secretion and cellular respiration in stem cell derived beta-like cells.
Mel1 HNF1A WT, HET and KO ESCs were differentiated into pancreatic endocrine cells and analyzed as described below.
(A–C) Glucose stimulation insulin secretion (GSIS) in HNF1A allelic series at end stage of differentiation (n=4 per sample). (A) Stimulation index of insulin secreted showing fold change 20mM over 2mM glucose. (B) Quantification of insulin secreted per insulin positive cell in femtomoles (fM), low glucose (LG) 2mM and high glucose (HG) 20mM. (C) Stimulation index of insulin secreted in HNF1A KO cell line comparing LG to HG or HG plus 20uM Tolbutamide (n=3 per sample).
(D–F) Glycolysis stress test for HNF1A allelic series (n=3 per sample). (D) Glycolytic profile of HNF1A allelic series showing as a extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) normalized at basal levels. (E) Glycolysis quantification. (F) Glycolysis capacity quantification.
(G–H) Mitochondria stress test (n=3 per sample). (G) Mitochondrial respiration profile of HNF1A allelic series obtained using oligomycin, FCCP and Rotenone/actinomycin (Rot/Act). (H) Quantification of maximal respiration capacity.
For all statistical analyses: * P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. See also Figure S4.