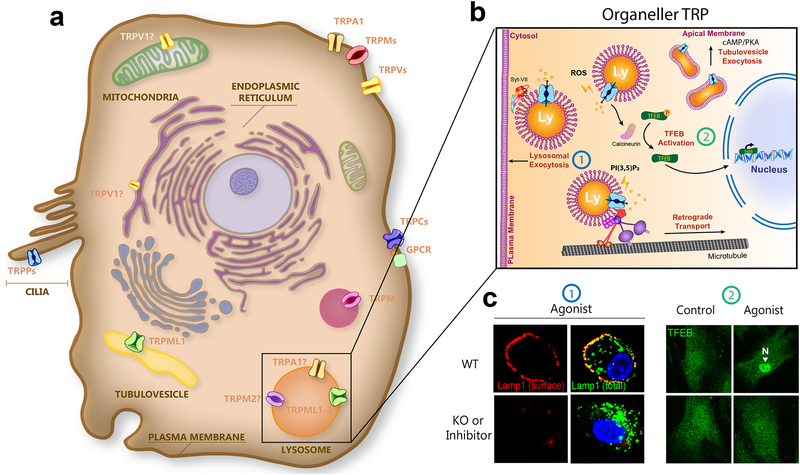
Fig. 3. Organellar TRP channels.
a. Though most TRPs are located at the plasma membrane, TRPMLs are localized in intracellular endosomes and lysosomes, and TRPPs are localized in primary cilia. In addition, TRPV1 is localized in the ER and possibly mitochondria, and TRPM7 is localized in M7-like vesicles. In specialized cell types, TRPA1 and TRPM2 are functionally expressed in lysosomes. In parietal cells, TRPML1 is an organellar TRP that functions in both lysosomes and tubulovesicles (TVs). b. Endogenous (e.g. ROS and PI(3,5)P2) or synthetic agonists induce TRPML1-mediated lysosomal Ca2+ release to trigger lysosomal exocytosis (example 1), retrograde transport, and TFEB nuclear translocation (example 2). In the parietal cells, histamine-induced cAMP/protein kinase A signaling activates TV-localized TRPML1, increasing TV trafficking and exocytosis. c. In example 1, activation of TRPML1 triggers lysosomal exocytosis, detected by the surface expression of Lamp1 proteins in WT, but not in TRPML1 KO cells. Images are modified with permission from ref.64; In example 2, agonist activation of TRPML1 leads to nuclear translocation of TFEB (green), a transcription factor for lysosome biogenesis and autophagy in WT, but not TRPML1 KO cells. Images are modified with permission from ref. 102.