Fig. 2.
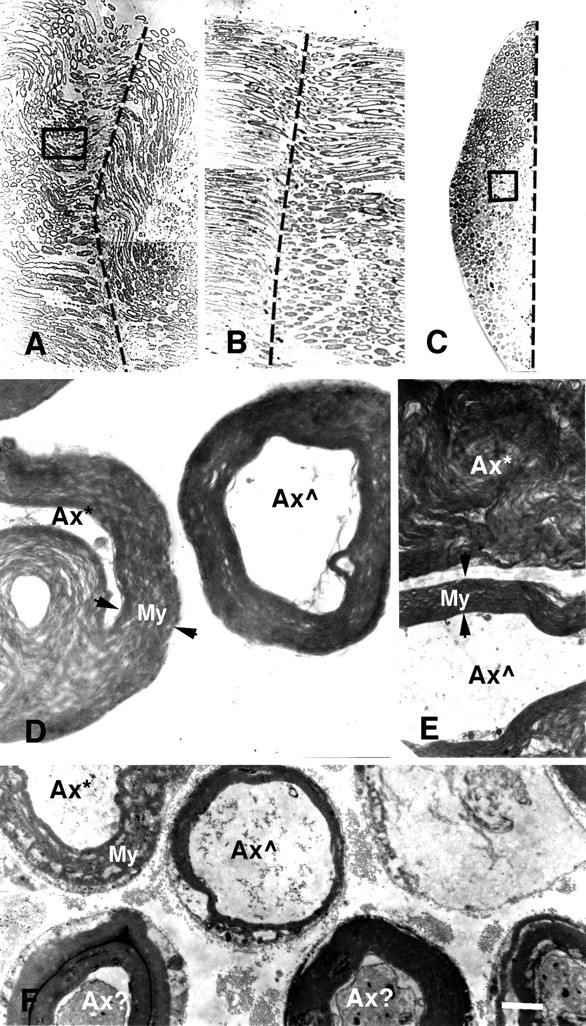
Photomicrographs (A–C) and electron micrographs (D–F) of longitudinal (A,B, D, E) and cross (C, F) sections of PEG-fused sciatic nerves after a complete cut (A,D, E) or crush (B,C, F). Vertical dashed lines in A–C show the site of severance and subsequent PEG application. Note that B andC are longitudinal and cross sections, respectively, taken through the site of PEG-induced fusion of a crushed sciatic nerve, of which a portion (box in C) is shown at higher magnification in F. As described in Materials and Methods and by Ballinger et al. (1997), the crushed sciatic axon was first sampled in longitudinal section (B) until a portion of the fusion site was detected (dashed line). The tissue was then remounted, and cross sections (C) were taken through another portion of the fusion site (dashed line).D and E are higher-magnification images of a portion of the cross section (box inA) of the entire sciatic nerve at the site of PEG-induced fusion. Axons exposed to PEG at the lesion site were in some disarray, and hence some individual axons were in transverse (D) or longitudinal (E) planes with respect to the long axis of an axon. Ax*, An axon with myelin or other membranes seriously delaminated, damaged, or dissolved by PEG; Ax , an axon with relatively intact axoplasm, myelin, and other membranes at the plane of PEG-induced fusion; Ax?, an axon with slightly damaged axoplasm, myelin, and other membranes at the plane of PEG-induced fusion;apposed arrowheads, the extent of myelin sheaths (My). For the cut axon shown in A,D, and E, the peak amplitude of the control CAP was 20 mV before the axons were transected. The CAP amplitude was 0 mV after the axons were cut in Ca2+-free hypotonic mammalian saline with 1.0 mm EGTA. A thin stream of 50% PEG 2000 kDa (Aldrich) was applied to the lesion site for 2 min. The preparation was then bathed in Krebs’ saline. Within 2 min after PEG application, the CAP was 0.5 mV, suggesting that PEG had induced fusion in a small fraction (2–5%) of crushed axonal ends. The CAP grew to 5 mV after the PEG-fused axons were maintained in Krebs’ for 1 hr, suggesting that as many as 20–30% of axons were now conducting through the lesion site. The sciatic nerve was then fixed as described in Materials and Methods. For the crushed sciatic nerve shown in B, C, and F, the peak amplitude of the control CAP was 14 mV before the axons were crushed. The CAP amplitude was 0 mV after the axons were crushed in Ca2+-free hypotonic mammalian saline with 1.0 mm EGTA. A thin stream of 50% PEG 2000 kDa (Aldrich) was applied to the lesion site for 1 min. The preparation was then bathed in the mammalian saline. Within 5 min after PEG application, the peak amplitude of the CAP was 1.0 mV, suggesting that PEG had induced fusion in a fraction (5–10%) of crushed axonal ends. The sciatic nerve was then fixed as described in Materials and Methods. Scale bar: A–C, 75 μm; D, 2 μm; E, F, 4 μm.
