Fig. 5.
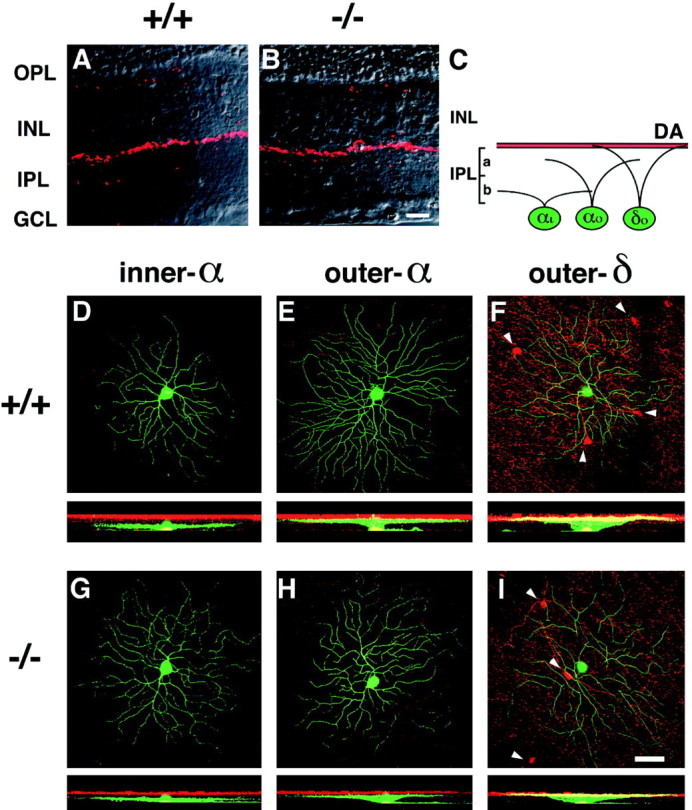
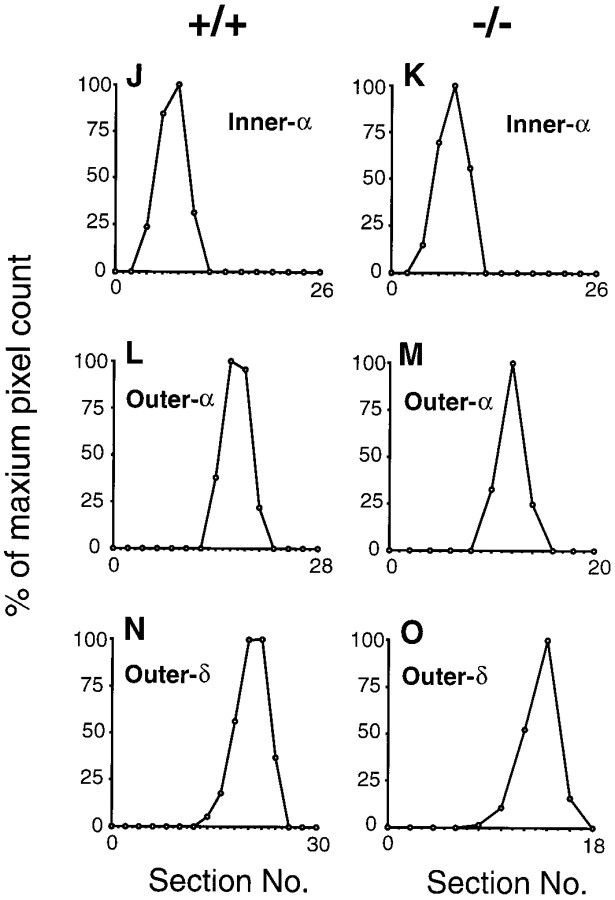
Dendritic morphology and stratification levels of inner-α, outer-α, and outer-δ RGCs in adult wild-type (+/+) and mGluR6 knock-out (−/−) mice. A, B, Dopaminergic amacrine cells immunostained with TH-Ab (red) were observed along the INL–IPL border in transverse sections of the two genotypes. This immunostaining was used as a reference to assign stratification levels of three types of RGCs (D–I). C, Stratification levels of three RGCs are schematically illustrated;αi, inner-α RGC; αo, outer-α RGC; δo, outer-δ RGC;DA, dopaminergic amacrine cell innervation.D–I, In each panel, the top shows a confocal image of dendritic branches of three cell types on the main dendritic x–y plane, and thebottom displays a reconstructed image on thex–z plane. Note that thex–z plane was processed to cut the GCL at the middle of RGC somata, thus they appear to protrude toward the IPL in D and G. green, LY-injected RGCs; red, immunostained dopaminergic amacrine cells. Somata of dopaminergic amacrine cells are indicated byarrowheads in F and I.J–O, Stratification levels and the distribution of dendritic branches of three cell types. For each cell, dendritic branches on each z-section taken from the GCL to the IPL–INL border (left to right in the abscissa) were represented as a percentage of thez-section containing the highest pixel count. The data were obtained from three types of RGCs shown in D–I. Eccentricity: D, 1.6 mm; E, 1.7 mm;F, 1.8 mm; G, 1.3 mm; H, 1.9 mm; I, 1.6 mm. Scale bars: B, 20 μm; I, 50 μm.