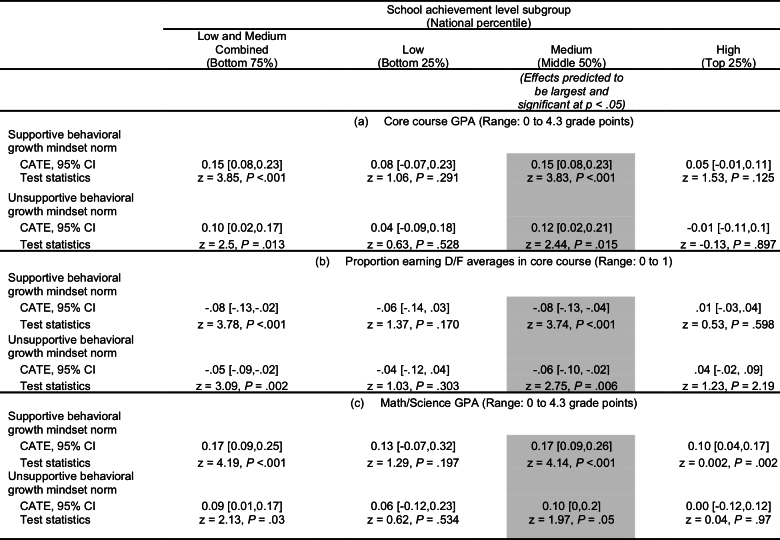
Extended Data Table 3.
CATEs are largest for medium-achieving schools with supportive norms
CATEs are the average differences between the randomly assigned intervention and control groups in terms of GPA or D/F average rates, for a given set of schools. 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. P values are from two-tailed hypothesis tests. Norms refers to behavioural challenge-seeking norms, as measured by the responses of the control group to the make-a-math-worksheet task. Standardized effect sizes for GPA are essentially identical to the unstandardized effect sizes because the standard deviation of GPA is approximately 1. The estimates were generated from the pre-registered linear mixed-effects regressions (equations provided in Supplementary Information section 7) that used survey weights provided by the research company to make estimates generalizable. The models included three school-level moderators of the student-level randomized treatment: the achievement level (categorical, dummies for low and high, medium group omitted), the behavioural growth mindset norms (continuous) and the percentage of racial or ethnic minority students (continuous) of the school. To define the school achievement levels for presentation of school subgroup effects, we followed the analysis plan. The pre-analysis plan did not include a method for post-estimation summarization of the effects of the continuous norms, so the table uses a prominent default: a split at the population median. The full, continuous norms variable was used to estimate the model, so the choice of the median split cut-off point did not affect the estimation of the regression coefficients. Grey shaded columns indicate the subgroup that was expected to have the largest effects in the pre-registered analysis plan. a, School achievement level subgroups for core course GPAs. b, School achievement level subgroups for reduction in rates of D/F averages in core course GPAs. c, School achievement level subgroups for GPAs of only mathematics and science.