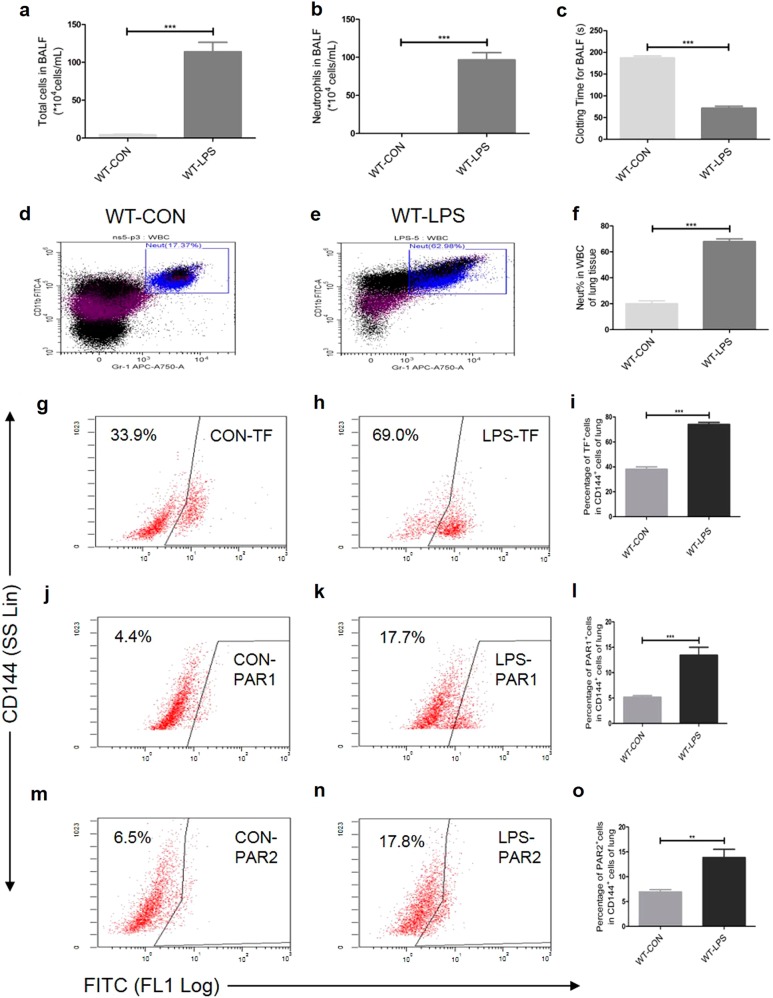
Fig. 1.
Intratracheal LPS induces lung inflammation (a-b, d-f), coagulation activation (c) and an increased expression of TF (g-i), PAR1 (j–l), and PAR2 (m-o) on CD144+ (the indicative molecule of ECs) cells in lung during ALI. Compared with NS group. n = 5–10 for each group. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns no significance. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three separate experiments. CON control, LPS lipopolysaccharide, ALI acute lung injury, WBC white blood cell, Neut neutrophil, BALF bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, TF tissue factor, PAR protease-activated receptor, ECs endothelial cells, WT wild type