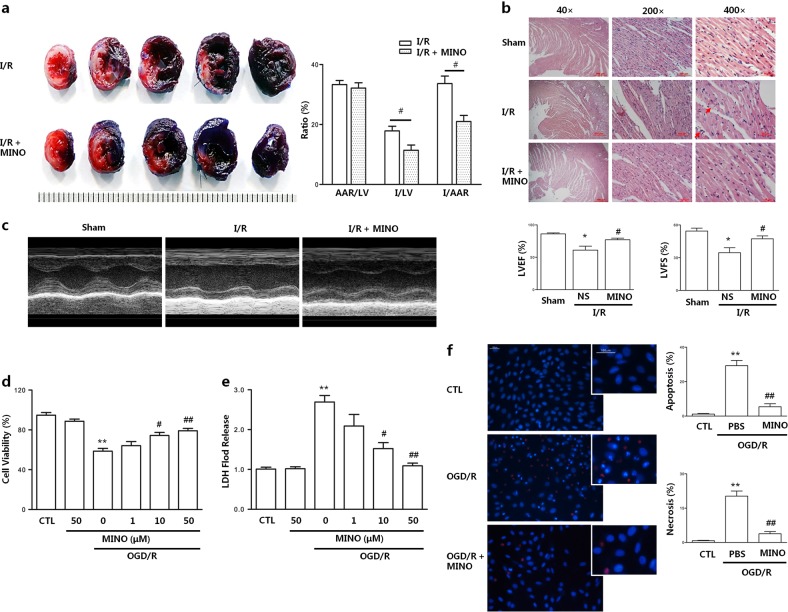
Fig. 1.
Minocycline protects cardiomyocytes against I/R-induced injury in vivo and OGD/R-mediated I/R injury in vitro. The infarct size, myocardial histology and cardiac functions were assessed in rats after I (1 h)/R (48 h). a Infarct images obtained by TTC staining. Non-ischemic myocardium was stained blue, the ischemic area was stained red, and the infarcted area was stained pale. b Histochemical sections of the left ventricle were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Scale bar = 500, 100, and 50 µm; c Cardiac function measurement was performed by echocardiography. Cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, apoptosis, and necrosis were assessed in H9c2 cardiomyocytes at OGD (6 h)/R (6 h) time. d Cell viability was analyzed by MTS assay. e Cell damage was determined by LDH release assay. f Representative figure of apoptosis (Hoechst staining showed bright blue nuclear condensation and fragmentation) and necrosis (PI-positive) as detected by Hoechst3324-propodium iodide double staining and the statistical graphs of apoptosis and necrosis. Scale bar = 100 µm; LVEF; left ventricle ejection fraction, LVFS; left ventricle fractional shortening. Values represent the mean ± SEM. n = 6–8 rats per group or 6 examples of cells; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the sham or CTL group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the I/R rats model group or OGD/R. CTL, normal control; OGD/R, oxygen glucose deprivation /reoxygenation