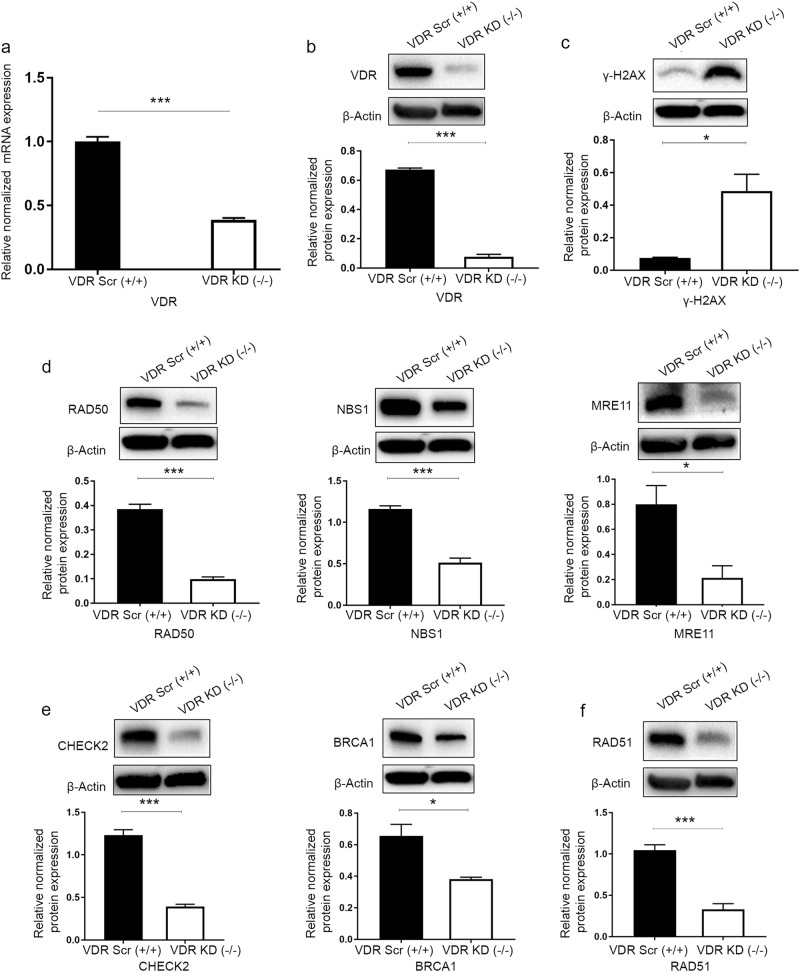
Fig. 3.
Vitamin D receptor (VDR) knockdown induced DNA damage and impaired the DNA damage response in uterine smooth muscle cells (UTSMs). VDR was targeted for knockdown in UTSM cells by infection with lentiviruses expressing VDR-specific shRNA (VDR KD) or scrambled control (VDR Scr). a Real-time PCR analysis was performed to determine the mRNA level of the VDR gene. The mRNA levels were normalized to 18 S RNA, and normalized values were used to generate the graph. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of triplicate measurements. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot analysis using antibodies against (b) VDR, (c) the DNA damage marker γ-H2AX, DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair-related markers, including homologous recombination DNA DSB; (d) sensors (RAD50, NBS1, MRE11); (e) mediators and effectors (CHECK2, BRCA1); and (f) DSB binding (RAD51). The intensity of each protein signal was quantified and normalized to the corresponding β-actin and presented in the graph as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0. 001. All experiments were repeated twice