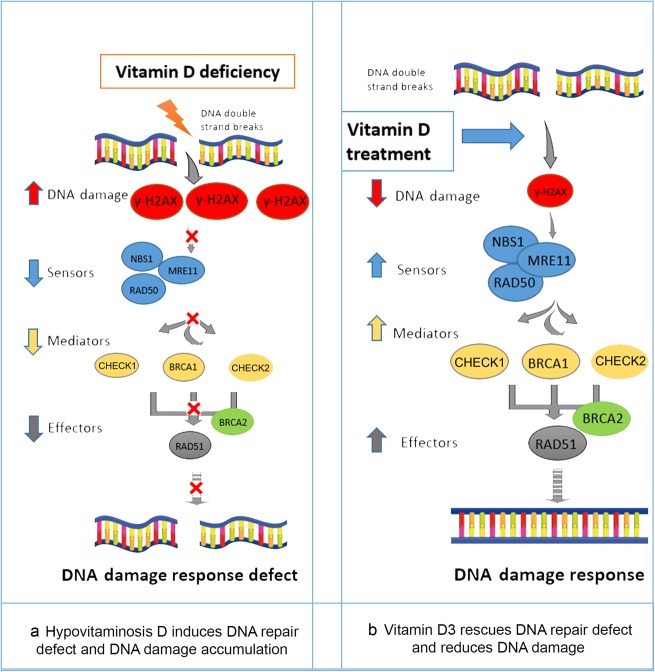
Fig. 8.
Model of the functional relationship between the vitamin D/VDR axis and DNA damage response. a Hypovitaminosis D induces DNA damage accumulation, as demonstrated by the accumulation of greater amounts of the DNA damage marker γ-H2AX and, consequently, DNA repair defects due to failed recruitment of DNA double-strand break sensors such as RAD50, MRE11 and NBS1, as well as effectors and mediators including CHECK1, CHECK2, BRCA1, BRCA2 and RAD51. This phenomenon results in DNA damage response defects. b Vitamin D3 treatment rescues DNA repair defects and reduces the DNA damage load by reducing the DNA damage marker γ-H2AX and recruiting key DNA repair proteins, including DNA double-strand break sensors such as RAD50, MRE11 and NBS1, as well as effectors and mediators including CHECK1, CHECK2, BRCA1, BRCA2 and RAD51, thus restoring the DNA damage response