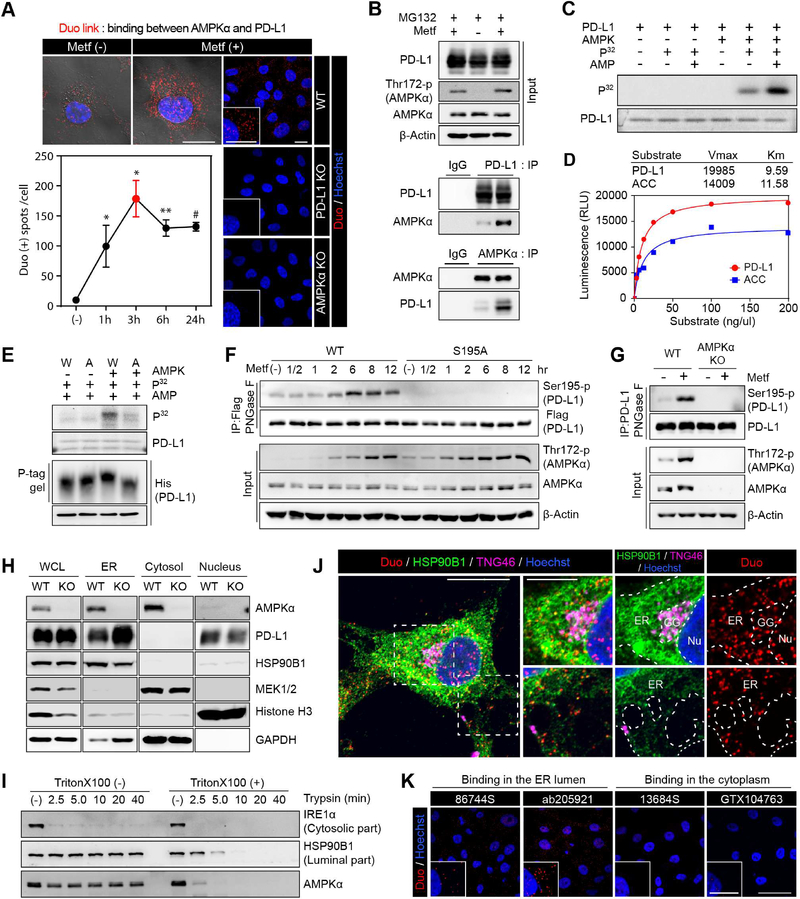
Figure 2. AMPK activated by metformin directly phosphorylates serine 195 of PD-L1.
(A) BT-549 cells were treated with metformin (5 mM) for the indicated time. Detection of endogenous AMPKα and PD-L1 binding (red dots) by Duolink II assay. Three different positions were randomly selected at each point, and the number of red dots were divided by the number of nuclei. Data represent mean ± SD. n = 3. *P, 0.01~0.05, **P, 0.001~0.01, and #P, < 0.001, Student’s t test. Scale bar, 20 μm. Right, MDA-MB-231 WT, PD-L1 KO and AMPKα KO cells were used as negative controls. Scale bar, 25 μm. (B) MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured for 6 hr with or without metformin (5 mM) and MG132 (10 μM). Endogenous PD-L1 and AMPKα were immunoprecipitated and their binding was analyzed with immunoblotting. (C) In vitro kinase activity of AMPK toward PD-L1 with 32P-labeled ATP. (D) Kinetics of PD-L1 phosphorylation by AMPK. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) was used as positive control. Km and Vmax were calculated using the Michaelis-Menten equation. (E) In vitro phosphorylation assay and phospho-tag gel shifting assay. W, PD-L1/WT. A, PD-L1/S195A. (F) PD-L1/S195 phosphorylation was examined using anti-PDL1/S195-p antibody at different time points after metformin (5 mM) treatment. (G) Western blot analysis of MDA-MB-231 WT and AMPKα KO cells after metformin treatment (5 mM) for 8 hr. Endogenous PD-L1 purified by IP was subjected to immunoblotting with PDL1 S195-p antibody after PNGase F reaction. (H) PD-L1 and AMPK subcellular localization of MDA-MB-231 WT and AMPKα KO cells. (I) Trypsin digestion of ER fractions with or without permeabilization. (J, K) BT-549 cells were treated with metformin (5 mM) for 3 hr. (J) BT-549 cells were subjected to Duolink II assay combined with immunofluoresence staining using markers for ER (HSP90B1), Golgi (TNG46), and nuclei (Hoechst). Scale bar, 20 μm (inset, 10 μm). (K) Duolink assay with antibodies specific for ECD (Ab205921 and 86744S) and ICD (13684S and GTX104763) of PD-L1. Scale bar, 50 μm (inset, 25 μm). Red dots: AMPK-PD-L1 binding in (J) and (K).