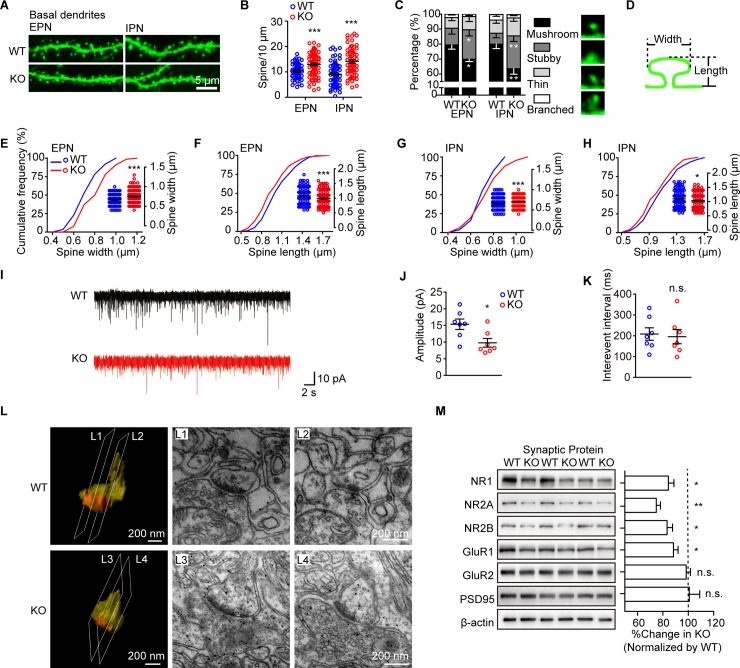
Fig 2. Dip2a KO mice display impairment in synaptic morphology and function.
(A) Representative images of THY1-GFP–labeled dendrites from EPN and IPN. (B) Increased dendritic spines density of basal dendrite in Dip2a KO mice (P56, males; 4 mice per genotype; EPN, WT = 59 neurons, KO = 75 neurons, t132 = 3.831, ***P = 0.0002; IPN, WT = 71 neurons, KO = 64 neurons, t133 = 5.819, ***P < 0.0001). (C) Reduced radio of mushroom-like spines (EPN, stubby, t132 = 2.004, *P = 0.0471; mushroom-like, t132 = 2.134, *P = 0.0347; IPN, stubby, t133 = 3.1443, **P = 0.0020; mushroom-like, t133 = 2.815, **P = 0.0056). (D) Illustration of the measurement of dendritic spine size. (E-H) Quantitative assessment of spine width or length (EPN, WT = 203 spines, KO = 183 spines; E, t383 = 5.991, ***P < 0.0001; F, t381 = 3.632, ***P = 0.0003; IPN, WT = 158 spines, KO = 201 spines; G, t357 = 3.864, ***P = 0.0001; H, t353 = 2.549, *P = 0.0112). (I) Representative whole-cell voltage clamp recordings of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) (n = 7 mice per genotype). (J) Reduced amplitude of sEPSCs in KO mice (t12 = 2.751, *P = 0.0176). (K) No significant difference was observed in the interventional interval (t12 = 0.2820, n.s. P = 0.7828). (L) Examples of 3D reconstruction depicting postsynaptic structure and electron micrographs. (M) Western blot showing the PSD fraction (4 mice per genotype in each experiment; data from 4 independent experiments). Protein levels were normalized to β-actin. The ratio in WT mice was set to 100% (NR1, t18 = 2.274, *P = 0.0355; NR2A, t10 = 4.156, **P = 0.0020; NR2B, t10 = 2.248, *P = 0.0484; GluR1, t18 = 1.082, *P = 0.0447; GluR2, t18 = 0.8829, n.s. P = 0.3889; PSD95, t10 = 0.0759, n.s. P = 0.9410). Data are represented as mean ± SEM and assessed with two-tailed unpaired t test. The underlying data for this figure can be found in S1 Data. Dip2a, disconnected-interacting protein homolog 2 A; EPN, external layer of pyramidal neurons; GFP, green fluorescence protein; GluR1, glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 1; IPN, internal layer of pyramidal neurons; KO, knockout; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NR1, NMDAR1; NR2A, NMDAR2; NR2B, NMDAR2B; n.s., no significance; PSD, postsynaptic density; THY1, thymocyte antigen 1; WT, wild-type; 3D, three-dimensional.