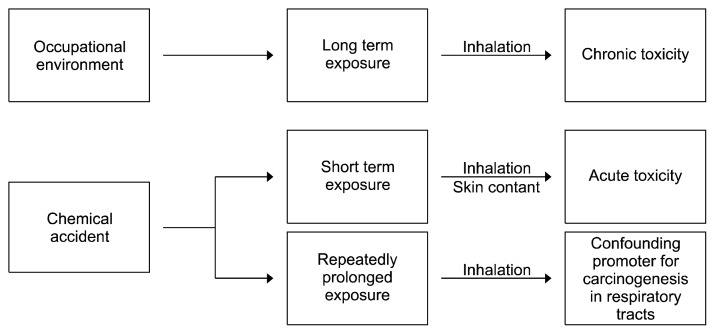
Figure 1.
A diagram showing the overall toxicity and major routes of chronic and acute exposure to sulfuric acid mists caused by workplace environments and chemical accidents. In occupational environments, inhalation is a potential route of exposure since mist display gaseous characteristics and are widely dispersed throughout respiratory airways. During chemical accidents, skin contact and inhalation are potential routes for short-term and/or repetitive prolonged exposure. Once sulfuric acid mists come in contact with air, it may persist in nearby locations and neighborhoods causing prolonged exposure. Therefore, sulfuric acid mists are regarded as confounding promoters for the induction of respiratory tract cancers.