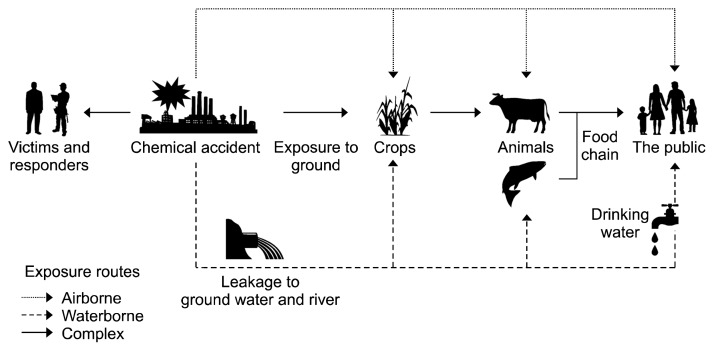
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram illustrating the potential pathways of exposure for sulfuric acid mists in caused by a chemical accident. A fate model represents the major pathways of exposure during accidents with sulfuric acid mists that can be dispersed when they come in contact with air or waterways. After an incident occurs, a response is launched to decontaminate and mitigate adverse health effects, but there is still a risk of repeated and prolonged exposure for responders, victims, and the general public due to airborne and waterborne contamination.