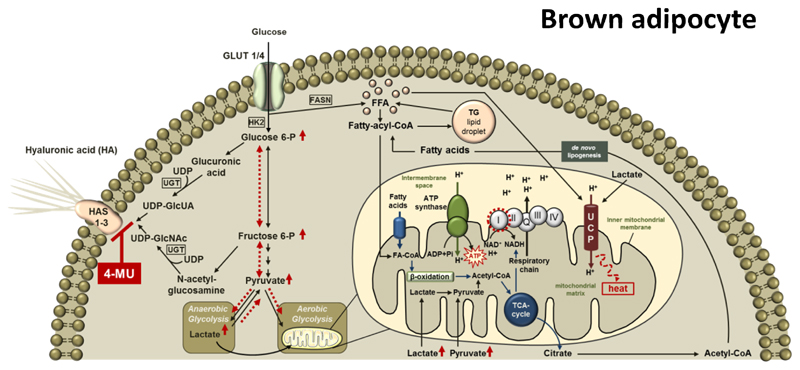
Figure 7. Proposed mechanism of action of 4-MU in brown adipose tissue.
Hyaluronan (HA) is synthesized from the UDP-sugar precursors, UDP-glucuronic acid (UDP-GlcUA) and UDP-N-acetyl-glucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) by three HA synthase (HAS) isoenzymes, HAS1, -2 and -3. 4-MU inhibits HA synthesis by competing with the HA precursors for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) thereby changing the intracellular substrate flux as indicated by red, dashed arrows. Sugar precursors, which are no longer used for HA synthesis, are directed into glycolysis finally leading to increased amounts of pyruvate and lactate. Lactate itself increases Ucp1 mRNA expression while pyruvate is directed into the mitochondria and utilized by the TCA cycle, providing NADH for the mitochondrial respiratory chain, subsequently resulting in increased state 3 respiration of complex I. In addition, TCA-derived citrate is used for de novo lipogenesis followed by free fatty acid-dependent UCP1 uncoupling.
HA: hyaluronic acid; HAS 1-3: hyaluronan synthase 1-3; UCP: uncoupling protein; GLUT: glucose transporter; HK: hexokinase; UDP: Uridine diphosphate glucose; UGT: UDP-glucuronosyltransferase; UDP-GlcUA: UDP-glucuronic acid dehydrogenase; UDP-GlcNAc: uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine; Glucose 6-P: glucose 6-phosphate; Fructose 6-P: fructose 6-phosphate; FASN: fatty acid synthase; CoA: coenzyme A; FA: fatty acids; FFA: free fatty acids; TG: triacylglycerol; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; ADP: adenosine diphosphate; AMP: adenosine monophosphate; Pi: phosphate; NAD: nicotine amide adenine dinucleotide; NADH: nicotine amide adenine dinucleotide hydride; TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle.