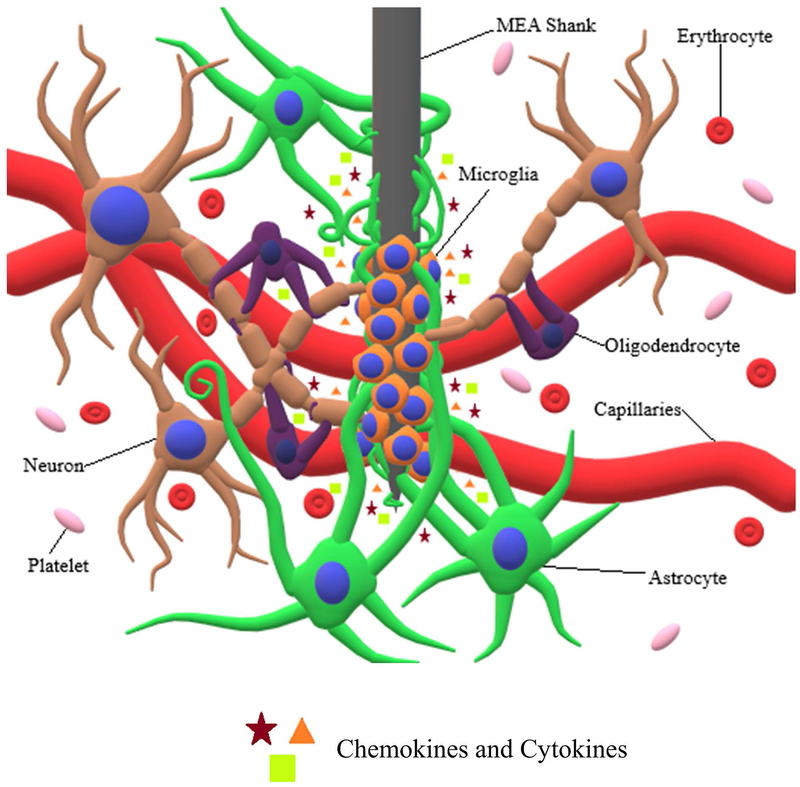
Figure 1:
Interaction of neuronal cells with MEA shank. MEA insertion causes severing of capillaries, cellular processes, and extracellular matrix, along with the release of erythrocytes and platelets. Additionally, the release of cytokines causes microglia and astrocytes to undergo morphological and behavioral changes. Microglia migrate towards the MEA shank and proceed to encapsulate it, while at the same time releasing proinflammatory cytokines and chemokine attractants. Following microglial encapsulation, astrocytes extend their processes towards the MEA shank, proceeding to encapsulate both the microglia and MEA shank.