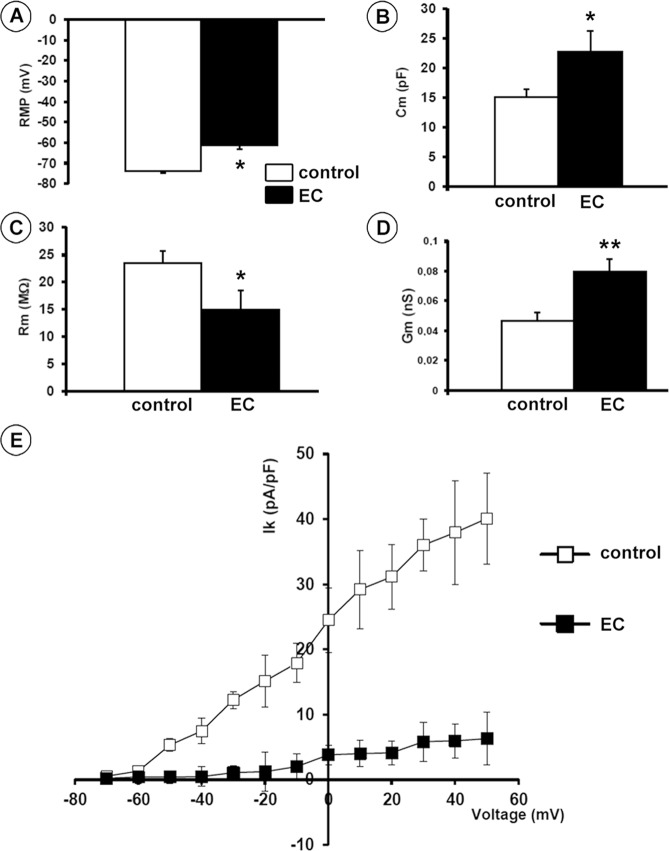
Figure 2.
Electrophysiological analysis of the sarcolemnic properties of control and eccentric contraction (EC)-damaged skeletal muscle fibers. (A) Resting membrane potential (RMP) recorded in the current clamp mode. (B–D) Membrane passive properties of the myofibers measured in voltage-clamp mode: linear capacitance, Cm, membrane resistance, Rm, and cell conductance, Gm. Data are reported as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control. (E) K+ current (IK) measured in voltage-clamp mode normalized to cell capacitance Cm (pA/pF). The IK values (means ± SEM) recorded in EC muscles, from −50 mV to 60 mV, were statistically different from those recorded in control muscles (P < 0.05). All measurements were performed on at least 15 myofibers from each of 5 control and 5 EC-injured muscles.