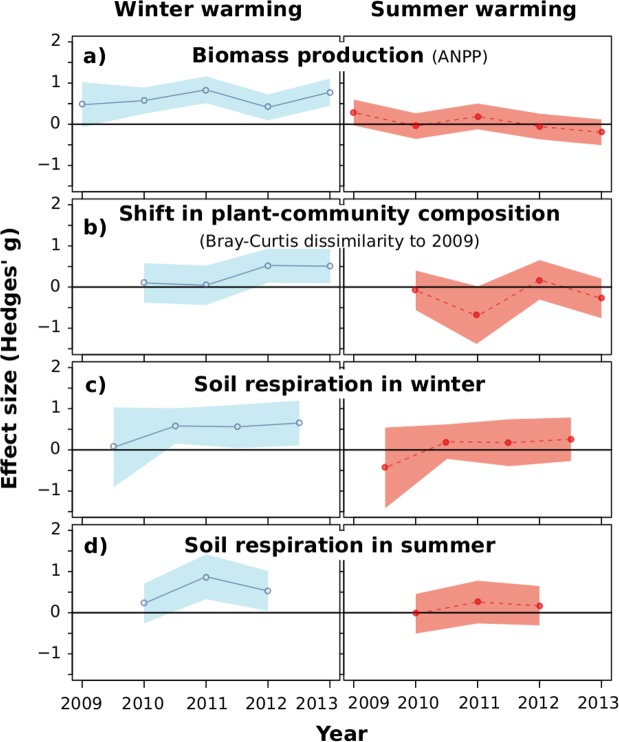
Figure 1.
Winter warming is ecologically more relevant than summer warming. (a) Aboveground net primary production (ANPP, sum of two destructive harvests of 0.2 m² y−1), (b) changes in plant-community composition per plot compared to its initial composition in 2009 expressed as Bray-Curtis distance (based on estimates of species-specific cover (1 m²) in June), and (c,d) soil respiration (mean of monthly measurements separated by winter (c) and summer (d) for the entire study period). The effect sizes as compared to reference conditions are displayed as Hedges’ g (n = 10) per sampling date and treatment and its 95% confidence intervals. A treatment is considered significant if the confidence band does not include zero (gray horizontal line). Note that the year 2009 displays pre-treatment conditions.