Figure 2.
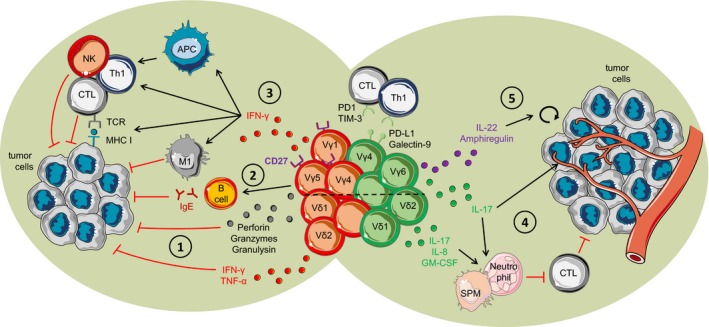
Pro‐ and antitumor effect of γδ T cells. (1) Antitumor immunity of γδ T cells by direct killing of tumor cells via perforin, granzymes, granulysin and cytokines. (2) Vγ5+ γδ T cells induce B‐cell class switching to autoreactive antitumor IgE. (3) IFN‐γ production by γδ T cells promotes the recruitment of NK, Th1 and CTLs and induces the differentiation of antitumor macrophages. Additionally, IFN‐γ enhances the presentation capacities of APCs and MHC I expression by tumor cells, while inhibiting pro‐tumor T helper cells. (4) γδ T cells producing IL‐17 promote angiogenesis and suppress antitumor CTL and Th1 cells. (5) Production of IL‐22 and amphiregulin by γδ T cells induces direct tumor cell proliferation. The dashed line separates mouse and human γδ T cells. γδ T cells depicted in red are the cells with antitumor functions, while γδ T cells depicted in green are the cells that promote tumor growth.
